-
Posts
2,401 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
91
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Blogs
Events
Status Replies posted by richardmurray
-
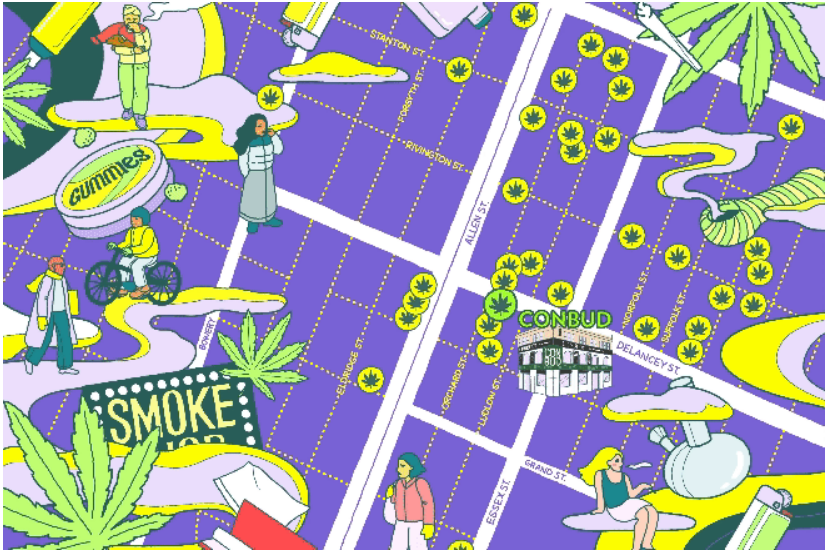
Weed Gone Wild: 34 Cannabis Shops — But Just One Licensed — on the Lower East Side
New York’s marijuana legalization was supposed to bring order and justice to the market. Instead, one year later, it’s created a confusing potpourri of vendors.
BY ROSALIND ADAMS
JAN. 5, 2024, 6:00 A.M.
A map shows unlicensed Lower East Side cannabis shops near state sanctioned smoke shop Conbud. Credit: Illustration by Naomi Otsu
This article is a collaboration between New York Magazine and THE CITY.
On a recent Friday afternoon, a line of people wrapped around a corner of Delancey Street waiting for a turn to get into Conbud, one of the city’s 15 legal weed dispensaries. It’s the kind of scene New York State lawmakers imagined would be commonplace when they legalized cannabis in March 2021: customers neatly queuing up at a limited number of suppliers.
But instead such crowds are a rarity outside Conbud, and this particular one wasn’t even there for the weed. People were there to see Mike Tyson, the boxer, who grinned and flexed with fans inside to promote the New York launch of his cannabis brand.
On line, I met Vinay, 23, who had invited a group of his college buddies to the event. “My roommate sent me the email, and my friends are in town, so why not?” Vinay told me. “We love weed, and Mike Tyson is cool,” one of his friends interjected.
While we chatted, dispensary staff moved through the line with iPads to take orders (a purchase was required to snap a photo with Tyson). Vinay told me he had never been to Conbud before. He said he usually bought weed from one of the smoke shops a couple blocks away on Clinton Street. None of those are licensed to sell cannabis products, though. When I mentioned this, Vinay shrugged.
“I guess if I knew it was illegal, I wouldn’t go, but you don’t realize,” he said.
There are, in fact, only 43 legal retailers across the state, including delivery operations — and they are all run by people impacted by cannabis charges. When lawmakers legalized pot, they intended to give those harmed by prohibition a head start in the market. But a year after the first legal store debuted near Astor Place, the pace of licensed dispensary openings has been painstakingly slow.
Just to open their doors, legal dispensaries had to overcome a gamut of regulatory hurdles that came with a steep price tag. Anthony Crapanzano, who has a dispensary license in Staten Island, said he has racked up about $1.6 million in expenses so far, including $200,000 in legal fees, and is still not open. Coss Marte, the owner of Conbud, said he’s spent more than $1 million getting ready to open.
Once in business, state-approved weed shops can only carry products cultivated by New York farmers and are subject to strict regulations on how they market their goods. Neon colors, bubble letters, and colloquial references to cannabis itself are barred from store advertisements. Everything must be tested — and taxed.
While the cannabis-impacted entrepreneurs waded through Albany’s new marijuana bureaucracy, an estimated thousands of unlicensed smoke shops popped up in New York City. Because there’s little oversight, the exact number remains unclear. Around Conbud alone, rival smoke shops and weed bodegas line the blocks, flouting the rules with their white fluorescent lights and bright signage that make them so instantly recognizable as cannabis stores with names like Zaza City and Smoke Kave.
These unlicensed shops can be cheap and easy to set up (some keep just a small amount of product in the store in case they’re raided). And unlike their legal counterparts, the unlicensed stores don’t pay state taxes on cannabis sales, which means their weed is often cheaper. Some of them try to get around the regulations by operating as private membership clubs where pot isn’t sold outright but “gifted” or held onto for a friendly patron. Others are bodegas that dedicate a small amount of shelf space to cannabis products alongside the usual offerings of pints of ice cream and cans of Arizona iced tea.
The rapid rise of unlicensed shops has alarmed lawmakers who are trying a number of solutions to deter them. This past February, the Manhattan DA sent out letters warning more than 400 smoke shops that they could be evicted for unlicensed activity. In June, the Office of Cannabis Management and the Tax Department began the first of hundreds of armed raids of shops around the state, seizing product and posting vibrant warning signs in store windows. The city has filed lawsuits against dozens of shops in Manhattan for allegedly selling cannabis to minors. The New York City sheriff, too, has been inspecting unlicensed shops and seizing their goods. While a few shops have shuttered, the sheer volume of stores is proving to be a difficult test of these efforts.
THE CITY and New York counted at least 33 stores selling cannabis within a few blocks of Conbud on the Lower East Side. We visited five of the stores in the neighborhood to learn more about how the weed market has developed a year after the first legal sale of cannabis in the state.
Conbud – The Sole Licensed Dispensary
Conbud, which finally opened in October, is the only licensed dispensary in the neighborhood so far. Owner Coss Marte, who has three felonies for dealing drugs, was awarded a special license back in April. But after a lawsuit challenged the legality of the license program, a court injunction prevented stores from opening for months. Marte’s plans for a summer launch were derailed. Meanwhile, he and other licensees were racking up expenses paying pricey New York rents for idle storefronts.
In the meantime, the delay gave unlicensed stores an opportunity to gain more of a foothold in the neighborhood, Marte acknowledges. “The market has already matured in the Lower East Side specifically. Some of the stores around here have already been open two or more years,” he told me. “Consumers are just thinking that this is what it is, not that the stores are illegal.”
Inside, the shop borrows a lot from Marte’s personal story: There are product displays reminiscent of the milk crates he used to sit on outside a bodega selling drugs. A full-screen television shows a loop of Marte at a local farm tending to cannabis plants that would soon be harvested and sold in the store, an employee told me. On one wall, the text of the 13th Amendment, which abolished slavery, is posted in bold letters. Conbud-brand T-shirts with the law’s text are available for sale, too. The effect is twofold: Marte is selling customers on the store’s cannabis products, like gummies marketed for sleep or energy and locally grown cannabis flower, but more broadly on the idea that legalization can be a form of reparation to those harmed by the war on drugs.
One of the most popular products is an ounce of Hudson Cannabis that’s grown upstate and runs for $185 — the best deal in the store but not as inexpensive as what some of the unlicensed shops offer.
A week before the Tyson event, Conbud threw a party to celebrate the launch of the Dr. Midtown brand, owned by a former legacy operator who goes by Nas. He told me he used to run a 1,200-person delivery route in Manhattan and was arrested in January 2021, right before the law changed. “I grew up in Queens, and it’s just been constant harassment,” he said. To see his brand now in stores, he added, “is exactly what we’ve been fighting for.” Promotional flyers for the party were printed with both Marte’s and Nas’s old mug shots along with the slogan “From Legacy to Legal.”
Part of the goal in hosting events like the one with Tyson and the launch party for Dr. Midtown is to educate people, Marte said. People living in the neighborhood see the long lines or hear the music and stop by to see what’s going on. That gives Marte an opportunity to explain that Conbud is the only legal cannabis store in the Lower East Side, he said.
“The more events we do, the more the community is aware that, ‘Hey, we’re here and we’re legal.’”
Flame Zone – A Shiny Smoke Shop
Shortly after Conbud opened in October, a flashy new smoke shop called Flame Zone Convenience appeared right across Delancey Street. The store employs several of the marketing techniques that legal stores are specifically prohibited from using. Its signage is written in a neon-green rounded bubble font. A sign advertised a grand-opening sale of an eighth of an ounce of weed for $20 (less than half what an eighth of Mike Tyson’s brand costs across the street), while another says the vape shop has the lowest prices around. If there was any doubt the store sold weed, there’s a towering inflatable joint just inside and a second one suspended from the ceiling.
Before Flame Zone opened, the business here was called Gee Vape and Smoke Shop. In February, Gee Vape was one of more than 400 stores the Manhattan DA warned in a letter could be evicted for selling cannabis. The store later closed. Flame Zone, according to the employee at the counter, is a different business from Gee Vape. “This is a new owner. She changed everything,” he told me.
While the shop may have a shiny new exterior, the property owner has been the same since 2007, city records show. Enforcement efforts have started to increasingly target landlords, not just the stores. But so far those measures have done little to deter a landlord from simply leasing the space to a new smoke shop. The volume of shops is simply too high.
In mid-November, shortly after Flame Zone opened, the Office of Cannabis Management and the New York State Tax Department raided the store. The two agencies are one part of the enforcement effort to curb the illegal shops. Last year, the state inspected 350 storefronts and seized more than $50 million worth of product, according to its latest figures LOOK BELOW. Though a pink slip from the raid is still posted in the door, it’s open for business.
Behind the counter, there are vape cartridges and pre-rolls branded with major California companies like Stiizy and Jungle Boys. House pre-roll joints are three for $20. When I ask the shopkeeper where the weed is from, he says, “Here, it’s in-house.” Only New York–grown weed is permitted in legal shops, and it remains illegal to transport cannabis across state lines. But for years California brands have faced allegations of “backdooring” their product to other states, and a number of websites sell counterfeit packaging from California brands down to a randomized serial number and QR code. That makes it hard for customers to know what they’re really buying.
Despite the bright lights and the low prices, the store still gets little foot traffic on a chilly December evening. In a half-hour or so, I see only one woman go into the store. She popped in while waiting for her order at Wingstop next door, she told me. When I asked what made her choose that particular store, she shrugged. “It’s just the closest one,” she said.
MetroBud – A Private Members Club
Owned by Joe and Jason Coello, two brothers from Queens, MetroBud on Allen Street operates as a private membership club. Blue velvet ropes guide customers to the entrance, and an employee checks IDs before letting anyone inside. The shop differentiates itself by encouraging people to stay awhile. Inside, two televisions loaded with video games are available to rent, and there are a few couches where you can just smoke and chill. MetroBud also hosts events like a weekly yoga class.
Joe Coello started planning to open the store as soon as legalization passed in March 2021, reasoning that a membership model was a way to get started without a state license. “We were trying to operate as above board as we could,” said Coello. “We were operating legally, as far as we were concerned.”
When the cannabis law passed, it included protections for people possessing weed as well as giving it away to their friends. Interpreting the latter to mean that they may legally “gift” weed to patrons or possess weed on behalf of members, cannabis membership clubs like MetroBud began popping up across the city. At one club I visited, customers pay for a photograph — and then are “gifted” cannabis in return.
There are no specific regulations that govern how the clubs operate because the distinction is not sanctioned by the state regulatory agency and there’s no specific license category for the model.
On many days, MetroBud seems to function like any other weed store. Daily membership is effectively free, so anyone with ID can walk in off the street and make a purchase. On a recent Saturday night, there was little foot traffic and just one customer inside fixated on playing Mortal Kombat. The store carries various branded MetroBud strains of weed from New York farmers as well as other brands. Prices are divided by tiers and at the low end can beat prices that legal shops like Conbud offer.
The membership-club interpretation of “gifting” hasn’t been tested in court, but last year, the Office of Cannabis Management sent out letters warning operators that running unlicensed shops could potentially jeopardize their ability to get a license in the future. The letters specifically stated that a membership-club model was not allowed.
Despite the state’s warnings, Coello still hopes to go legal and has applied twice for retail licenses since opening MetroBud. “It would be nice just to not have to look over our shoulder,” he said.
Meanwhile, Coello defends his business model — and the crop of unlicensed shops in the neighborhood. “I believe in a free market,” he said. “As long as they’re putting out products that are safe and don’t have heavy metals, mold, or pesticides in them, I don’t see a problem with it.”
Allen Convenient Exotic – Twice Raided
Walk down Allen between Delancey and Broome Streets, and you’ll find two more smoke shops near MetroBud: Green Apple Cannabis Club and Allen Convenient Exotic. Red, green, and purple lights from the trio of stores overwhelm passersby. As I stood outside on a recent evening, I watched a couple point to the fluorescent lights. “Why do all these places look so ugly?” one asked.
Cannabis was legalized just one year into the pandemic, as restaurants and retail shops were struggling to stay afloat. Some smoke shops have opened in place of establishments that stopped paying rent in the pandemic. The space occupied by Allen Convenient Exotic had been a smoke shop for years, selling items like vapes and glass pipes and cigarettes. But Green Apple Cannabis Club used to be a clothing store, and MetroBud was previously a pop-up space hosting events from brands including PornHub and Subway.
The three stores are an example of how ineffective state enforcement has been in curbing unlicensed sales. While Green Apple and Metrobud’s owners both say they’ve never had any major issues with state or local law enforcement, Allen Smoke Shop has a poster in the window with loud red letters: ILLICIT CANNABIS SEIZED. The store has been raided at least twice by state officials, according to the posted notices.
To allay any doubt that it still sold cannabis, the shop projects a roving image of the cannabis plant on the sidewalk outside.
Inside, there’s a wall of sodas and chips and even a small shelf of Bounty paper towels as in any other neighborhood bodega. Much more discreetly than in a place like MetroBud, the cannabis products like THC-laced edibles as well as “mushroom extract” gummies are confined to just a small section at the front counter. With a few cannabis-plant signs in the window and a bit of shelf space, the shop is an example of how easy it is for owners to add on a few products. When I snap a photo with my phone, it immediately catches the attention of the shopkeeper. “Hey, no photos. You can’t take a photo in here.” With the flip of a switch, the clear glass counter turned a frosted white, concealing the contents from view.
Dubai Cannabis Supply – Sued by NYC
I head over from Allen to Stanton Street, which has its own row of unlicensed shops selling cannabis. I pass by a few of them and head into Dubai Smoke, which the city sued in July, to see how it’s currently operating.
The complaint cited three instances in which the shop allegedly sold illegal psilocybin products. Created in the 1970s as a means to shutter undesirable businesses like places of prostitution, the nuisance-abatement law is one more tool the city has to curb illicit cannabis shops. In 2023, it filed at least 35 cases against smoke shops and their landlords for selling cannabis products to minors. Inspections are typically carried out by the NYPD, which documents at least three instances of the unlicensed activity before seeking a court order to close the store for one year. The city settled with Dubai in November on the condition that it would not sell unlicensed cannabis or tobacco products.
But a December visit shows that’s plainly not the case yet. Inside, the shop looks like the color palette of a Jojo Siwa concert. The walls are covered in rainbow graffiti, and under the glass cases there are glass tubes of pre-rolled joints for $20 labeled ZKITTLES. The man at the counter pulls out the tray of ones that come in flavors labeled Cotton Candy, Jungle Juice, and Froot Loops. A row of vape cartridges has options in lilac and teal and fuchsia. There are more California brands, like Stiizy gummies, on display here, too. None of these rainbow offerings would be allowable at the neighborhood’s one legal dispensary, Conbud.
Outside, I spot a group of what appear to be teen boys passing a joint among them. I nod to the joint and introduce myself as a reporter working on a story about cannabis shops in the neighborhood.
One tells me loudly they’re all 21 before laughing.
“Bro, no you’re not, no you’re not,” one of them shouts.
“Okay, yeah, we’re all 16.”
“I’m actually 35,” says a third. (I start to believe they are indeed 16.)
Dubai Smoke Shop wasn’t cited for selling to minors, but at least 34 other shops in Manhattan last year were, according to a review of nuisance-abatement complaints. This has been a rallying cry of lawmakers looking to shut down unlicensed shops with no oversight of its sales.
When I asked the teens where they liked to go for weed, they brushed me off. “I mean wherever they will sell to us, there’s only a few places around here,” one said.
“We’re not gonna tell you which ones.”
Article link
https://www.thecity.nyc/2024/01/05/weed-gone-wild-cannabis-lower-east-side/New York Fined Unlicensed Weed Shops More Than $25 Million — and Collected Almost None of That
Gov. Kathy Hochul has said she wants to shut down the illegal stores, but the lack of enforcement reveals just how hard that task will be.
BY ROSALIND ADAMS
FEB. 22, 2024, 5:00 A.M.The state has levied more than $25 million in fines against unlicensed smoke shops for selling cannabis products since last year, but so far only a minuscule percent of those fines have been collected by both the state Tax Department and the Office of Cannabis Management, THE CITY has learned.
The two agencies were granted greater authority last year to enforce the 2021 cannabis law and began joint raids against smoke shops for selling cannabis products without a license last summer. They levy and collect fines separately, however. Fines may be levied against individuals who operate the smoke shops or the business itself when it’s difficult to track down an owner.
The Office of Cannabis Management (OCM) said it has collected $22,500 in fines from unlicensed shops. The Department of Taxation and Finance has collected $0 in fines so far, said sources familiar with the state’s enforcement progress.
Last October, THE CITY reported that the state cannabis agency, citing a lack of resources, had paused the enforcement hearings that follow state agency raids on unlicensed shops. Lawyers for unlicensed shops told THE CITY at the time that they had received notices on behalf of their clients that the cases were being withdrawn. Meanwhile, the raids have continued.
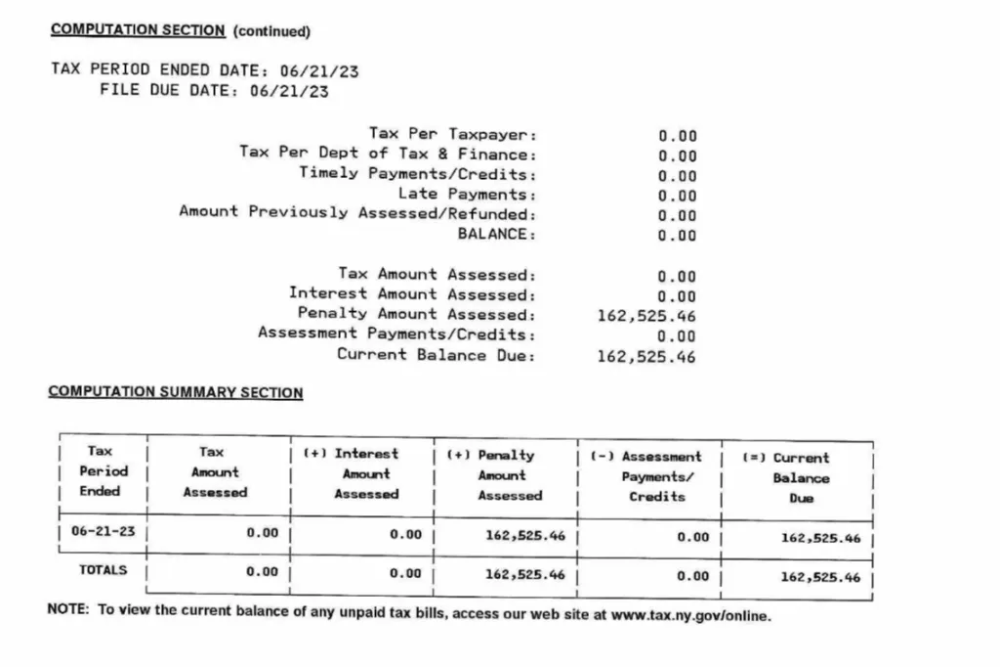
But while OCM has withdrawn many cases, some shops and their operators have separately received letters separately from the tax department warning them of fines more than $150,000, according to notices obtained by THE CITY.
“Currently, the State is prioritizing shutting down illegal shops and seizing unlawful products,” said Aaron Ghitelman, a spokesperson for OCM. “While we recognize entities being fined have a right to due process, we are committed to working within the confines of the law to collect the fines once the legal process is complete.”
Fines levied by the tax department may be appealed, for example. And shops fined by the Office of Cannabis Management may be challenged in the administrative hearings the agency paused back in October, which lengthens the state’s timeline to collect the fines.
Ghitelman added that the state has seized tens of millions of dollars in illicit products as part of its enforcement measures. Gov. Kathy Hochul has repeatedly emphasized the amount of product seized in press releases about the progress of the raids.
The governor’s office and the state tax department declined to answer questions and deferred to the statement provided by OCM.
The dearth of fines collected so far highlights the challenge of enforcing the cannabis law in a state with a booming gray market.
In New York City alone, unlicensed shops are rampant throughout some neighborhoods. Though there is no official count of the number of unlicensed smoke shops, it is estimated to be in the thousands. Last month, local news outlet CNY Central reported that OCM has only 14 investigators on staff.
The two state agencies are not the only ones involved in enforcement. The Sheriff’s Department is inspecting smoke shops in New York City as well, and the NYPD has done undercover inspections of shops suspected of selling cannabis to minors.
In Hochul’s annual state of the state address last month, the governor said that she would seek new enforcement powers this year as part of the annual budget.
“We know there’s more to be done and we need more tools to do it. We’re going to continue working with local leaders, including in New York City, to shut down illegal cannabis stores once and for all,” she said.
Sen. Jeremy Cooney, the chair of the Senate Cannabis Committee, agreed that more enforcement powers are needed, but added that the effort has to be in tandem with opening up new stores.
“The way forward is to make sure that we have more legal stores operating on our streets,” Cooney told THE CITY in an interview. “It’s a parallel track – one is to close down stores and make sure enforcement is happening, the other is to make sure that new ones are opening.”
“We’re not moving fast enough,” Cooney added.
At a Senate hearing in late October, executive director Chris Alexander testified that he did not think fines were enough to deter unlicensed shops. In response to questions, he said that he expected OCM’s administrative hearings to resume within weeks. But months later, the hearings have not resumed. OCM said it is seeking expanded enforcement powers to padlock stores instead of issuing fines.
Sen. Cooney told THE CITY he was unaware of this and found it “very concerning.”
The fines levied by the Tax Department are determined by a formula that assesses that unlicensed shops owe up to two times the amount of tax that would have been due on that illicit cannabis, the deficiency notices said.
Both letters reviewed by THE CITY say that more than 12 pounds of illicit cannabis had been seized but do not show specifically the details of the calculation. The law affords people the right to appeal the fines, which may be part of the reason why the agency has not collected any fines from unlicensed shops yet.
But in both instances, the shops had been raided by the OCM and the Tax Department and had product seized but the state cannabis agency had withdrawn their proceedings.
“Of course no one is paying them,” said Paula Collins, a lawyer who represents clients who operate unlicensed smoke shops. “They thought it was over.”
URL
https://www.thecity.nyc/2024/02/22/new-york-state-hochul-fines-illegal-cannabis-shops/CANNABIS FIGURES
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: December 4, 2023
CONTACTS: Aaron Ghitelman /Aaron.Ghitelman@ocm.ny.gov / 518-728-9570
NEW: OFFICE OF CANNABIS MANAGEMENT NOVEMBER ENFORCEMENT UPDATE ON STATEWIDE ACTIONS AGAINST UNLICENSED CANNABIS SHOPS The Office of Cannabis Management and the Office of the Attorney General win major court victory; new precedent set for State to use Cannabis Law to permanently close illegal businesses More than $50 million worth of illicit cannabis seized to date Additional court victory and new trainings for localities also announced NEW YORK, NY – Today, the New York State Office of Cannabis Management (OCM) published the second in a monthly series of enforcement action updates against unlicensed cannabis shops across the State. These updates will be released on the first Monday of each month through the end of the year. Inspections & Seizures: During the month of November, investigators from OCM and the Department of Taxation and Finance (DTF) inspected 71 shops, including 13 re-inspections, suspected of selling unlicensed cannabis. These inspections resulted in the seizure of 812 pounds of flower, 701 pounds of edibles, and 61 pounds of concentrate, with an estimated value of $7,284,986. These actions bring the total of inspections to 350 locations, 88 of which have been re-inspected, to yield over 11,000 pounds of seized illicit cannabis worth more than $54 million. OCM and DTF investigators will continue inspections each and every week across the State. Court Victories: On November 21, OCM, in collaboration with the Office of the Attorney General (OAG), won its first petition for emergency relief under Section 16-a of the Cannabis Law, a new section of the law that just went into effect this year. This victory established an important precedent allowing the State to seek longer term closures for businesses found to be illegally selling cannabis. In this case, the Court issued a permanent injunction and one-year permanent closing order against illegal operator David Tulley of "I'm Stuck" in Wayne County. The Court agreed with OCM and the OAG that Tulley had engaged in unlicensed sale of cannabis and rejected Tulley's argument that the “cannabis consulting business model” did not require a license. The Court’s Order continued the padlocking that had been granted by the Court on an emergency basis earlier this year. An assessment of total penalties will be finalized in the coming weeks. On November 29th, OCM, in collaboration with the OAG, also successfully secured a temporary restraining order and temporary/closing/padlocking order against the unlicensed operator George West of Jaydega 7.0 in Canandaigua. A hearing on the request for a permanent injunction and closure of Jaydega 7.0 is scheduled for next month in Ontario County Supreme Court. Training for Municipalities: With a continued focus on collaboration and coordination with the goal of maximizing enforcement partnerships, OCM and the OAG will host a public webinar for municipalities across the state on Thursday, December 7 to provide vital education and resources around best practices and opportunities to shut down illicit operators. “As we look ahead to this next chapter in New York’s cannabis market, we continue to prioritize safety across the state by working diligently to shut down illegal operators,” said Chris Alexander, Executive Director of The New York State Office of Cannabis Management. “The number one remedy for the problem of these illicit shops is getting more legal businesses open. New Yorkers want to know where their products are coming from, and they know they can rely on safe, trusted, and locally grown cannabis when they walk into one of our legal dispensaries. We will continue to seize illegal products, and we know that the collaborative work continues across all levels of government to address this public health crisis.” Fines for the illegal sale of cannabis start at $10,000 per day and can rise up to $20,000 per day for the most egregious conduct. An additional fine of $5,000 can be levied for removal of the Order, and the inspected businesses may also be subject to additional violations and penalties under the Tax Law. Additional fines may be assessed. The enforcement legislation passed in May 2023 also authorizes OCM to seek a State court order to ultimately padlock businesses found to be in repeated violation of the law. In addition, the law makes it a crime to sell cannabis and cannabis products without a license. To bring many levels of government together to combat the illicit sale of cannabis, Governor Hochul announced partnerships between OCM and the OAG through which municipalities across the state can receive training on how to utilize a particular provision -- Section16-A -- of the new enforcement law signed by Governor Hochul in May 2023 to pursue padlocking orders in State Court. 16-A authorizes local governments, including county attorneys, with OCM’s approval, to pursue padlocking orders from a court against an unlicensed cannabis business found to be engaged in egregious conduct. This authority significantly augments the ability for different levels of government to work together to shut down illegal cannabis operators. In addition to these new partnerships with localities, the Governor announced that additional State agencies will now be bringing the weight of their business enforcement powers to bear as part of the State’s creative and aggressive approach to combating the illicit market. The Department of Labor and the Workers Compensation Board are joining these efforts to ensure businesses selling cannabis without a license are compliant with New York State labor and workers compensation laws. This approach, which combines the enforcement powers of labor law, tax law, and cannabis law, can result in non-compliant business owners potentially facing tens of thousands of dollars in penalties as the result of a single inspection and violations, significantly enhances the State’s ability to crack down on those who engage in illicit sales, and reaffirms the Governor’s deep commitment to ensuring that the law is being followed and that New Yorkers are protected from potentially unsafe products. New York State currently has 27 licensed adult-use cannabis dispensaries and has approved 44 Cannabis Growers Showcases. All regulated, licensed dispensaries must post the Dispensary Verification Tool sticker near their main entrance. Any store selling cannabis that does not display this sticker is operating without a license. ### Follow us on all of our social media at @nys_cannabis
URL
-

Man cleared in a 1996 Brooklyn killing said for decades he knew who did it. Prosecutors now agree
By Associated Press New York State
PUBLISHED 9:36 PM ET Jan. 18, 2024
NEW YORK (AP) — A man who served 14 years in prison for a deadly 1990s shooting was exonerated Thursday after prosecutors said they now believe the killer was an acquaintance he has implicated for decades.
“I lost 14 years of my life for a crime that I didn’t commit,” Steven Ruffin told a Brooklyn judge after sighing with emotion.
Although Ruffin was paroled in 2010 and has since built a career in sanitation in Georgia, he said that getting his manslaughter conviction dismissed and his name cleared “will help me move on.”
“If you know you're innocent, don’t give up on your case — keep on fighting, because justice will prevail,” Ruffin, 45, said outside court. “That’s all I’ve wanted for 30 years: somebody to listen and really hear what I’m saying and look into the things I was telling them."
Prosecutors said they were exploring whether to charge the man they now believe shot 16-year-old James Deligny on a Brooklyn street during a February 1996 confrontation over some stolen earrings. Brooklyn District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said after court that charges, if any, wouldn't come immediately.
“You have to be able to convict someone beyond a reasonable doubt, and we have to make sure that that evidence is sufficient to do so,” said Gonzalez, who wasn't DA when Ruffin was tried. “You have a lot of factors working against us procedurally, but also factually — unfortunately, this is 30 years ago.”
Ruffin's conviction is the latest of more than three dozen that Brooklyn prosecutors have disavowed after reinvestigations over the last decade.
Over a dozen, including Ruffin's, were connected to retired Detective Louis Scarcella. He was lauded in the 1980s and ‘90s for his case-closing prowess, but defendants have accused him of coercing confessions, engineering dubious witness identifications and other troubling tactics. He has denied any wrongdoing.
Prosecutors said in their report on the Ruffin case that they “did not discover any misconduct by Scarcella" in the matter. A message seeking comment was sent to his attorney.
Prosecutors said the police investigation — and their office's own at the time — “were wholly inadequate” and tunnel-visioned, failing to look into the person they now believe was the gunman.
The mistaken-identity shooting happened as Ruffin and others were looking for a robber who had just snatched earrings from Ruffin’s sister. In fact, Deligny wasn't the robber, authorities say.
Tipsters led police to Ruffin, then a 17-year-old high school student, and the victim's sister identified him in a lineup that a court later deemed flawed. Scarcella wasn't involved in the lineup, but he and another detective questioned Ruffin.
The teen told them, twice, that he saw but wasn't involved in Deligny's shooting, according to police records quoted in prosecutors' report.
Then Scarcella brought the teen's estranged father — a police officer himself — to the precinct. The father later testified that he told his son to “tell the truth,” but Ruffin said his father leaned on him to confess.
And he did confess, saying he fired because he thought Deligny was about to pull something out of his jacket. Ruffin told the detectives they could retrieve the gun from his sister's boyfriend, and they did, prosecutors' report said.
Ruffin quickly recanted to his father, who didn't tell the detectives his son had taken back his confession, according to prosecutors' report. The teen went on to testify at his trial that he didn't shoot Deligny but saw and knew the killer — his sister's boyfriend, the one who'd given police the gun, broken up into parts and stuffed into potatoes.
Jurors at Ruffin's trial heard from the boyfriend, but only about his relationships with the defendant, his sister and others in the case. When the jury was out of the room, the boyfriend invoked his Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination and declined to answer other questions, including where he'd been on the night of the shooting.
Prosecutors didn't release the boyfriend's name Thursday, and the names of lawyers who have represented him weren't immediately available. He told prosecutors during their recent reinvestigation that he had nothing to do with the shooting and didn't give detectives the gun. He also said he never confessed to anyone, though prosecutors say Ruffin's stepfather, sister and late mother all have said he made admissions to them.
Asked Thursday about the boyfriend, Ruffin's lawyers noted that the prospect of any prosecution now is uncertain.
“We only wish that in 1996, Detective Scarcella and others had performed the investigation they should have and been able to get this right the first time," attorney Garrett Ordower said, noting that Deligny's family may now never have the finality of a conviction in his death.
As for Ruffin, he's focused on his future, including promotion opportunities at his job in Atlanta. His now-voided conviction, he said, “never defined me.”
“This never really spoke of the person I was or the man I was going to become,” he said. “So this, to me, is a great closure of a chapter my life, but my life is still going up.”
URL
-
Richard Murray Centos 2023
a poetry book, free top read, all inspirations are cited
https://www.kobo.com/us/en/ebook/richard-murray-centos-2023 -
Salvador, Bahia Festivals
January 2024

February 2024

-
Happy Perihelion
It will occur at 7:38pm Eastern standard time or UTC -5 the earth is the closest it will be to the sun, at 91,404,095 miles, and on its elliptical orbit about the sun, continuously increases the distance between the earth's center to the Sun's center, till the July aphelion
To see my 2023 art list use the following URL
https://rmnewsletter.over-blog.com/2023/02/2023-art-summary.html
A condensed form is the following Art vs Artist
https://www.deviantart.com/hddeviant/art/Art-Vs-Artist-2023-1007446039photo of sun from ben heine, title good morning

-

Enter our free and fun Best First Sentence Contest!
Each winner will receive a 10-page critique from one of the teachers of the Master Class. The deadline for entries is May 1, 2024.To enter the 2024 Best First sentence contest, please email your submissions to BestFirstSentence@gmail.com. You may only submit one entry. To qualify for entry you must be an ITW member or registered for ThrillerFest XIX (2024). Winners will be announced on Wednesday, May 29, 2024, at the CraftFest Luncheon and on social media. All winners will be notified shortly thereafter via email.
Watch our Animation Producing Course these holidays!
It's the end of the year, and we're thrilled to gift you with access to our course, Producing for Animation, designed to empower aspiring producers and creatives in the world of storytelling!You’ll get to learn what a producer really does, what an animation pipeline is, and how to manage creative teams, budgets, and schedules. All while working alongside a director to optimise the creative vision within the budget.
Best of all, it's completely free of charge, made possible through our donor, BMZ and partner GIZ.
Meet the Experts: Dianne Makings and Kaya Kuhn
Dianne Makings and Kaya Kuhn, two of South Africa’s most experienced animation producers, explain what a producer does and what skills and proficiencies are required in the role, as they guide us through each stage of a production, from bidding to broadcast.Dianne joined the animation industry after an 11-year career in advertising, PR and events. Not only does she perform the mammoth role of CTIAF’s festival director, but she also has produced a series of high profile projects. Her latest project; Aau’s Song was an original story produced for Lucasfilm. She has managed creative teams and processes for a variety of digital content including 2d, 3d, stop motion and VR. She is passionate about African animation and believes that the continent is more than ready for the global stage.
Kaya Kuhn started her career in the South African film industry in live action post-production where she notably post-produced six seasons of reality television series The Voice. In 2017, she took the leap into producing animation at Triggerfish. Since then, she line produced critically acclaimed short films Zog (BBC1) and The Snail and The Whale (BBC1), co-produced animated feature film Seal Team (Netflix), was involved with pre-production for animated series Supa Team 4 (Netflix) and Kiya & the Kimoja Heroes (Disney+), and most recently was the senior producer on the groundbreaking anthology Kizazi Moto: Generation Fire (Disney+) which is set to release in 2023. She was the consultant producer for animated short Aau’s Song which forms part of anthology Star Wars: Visions Volume 2 (LucasFilms) and has recently been involved in producing live action feature films for local broadcaster, Kyknet. Currently, she runs a production services company ‘Those Production Girls’ which offers high end production support through innovation and inclusion.
https://www.triggerfish.com/academy/
-
Response and Articles 12/19/2023
At the end of the war between the states: louisiana, south carolina, mississippi had majority black populaces, but the governments of said states had no black officials. One of the problems with some Black people in the usa is they speak very neutrally when it comes to humanity. Being verbose is a long thing, can be fatiguging, but is usually more descriptive and being more descriptive is needed when you speak of the past in humanity anywhere. The palestinean people had the majority in palestine when the zionist came but the government was completely run by members of the british empire. so...
I think a valid question exist. Beyond the law, did the 14th or 15th amendment's make the Black Enslaved or former enslaved citizens? What makes a citizen? is it the law? or is it, the communal context? I argue the history of the native american in the usa+ the black enslaved or descended of enslaved in the usa, refutes the idea that citizenry comes from the law.
The authors states tremendous progress for the black populace in what is commonly callted reconstruction in the usa, but i argue that is erroneous. First, most black people in the usa, 90% were still financially dead, no savings, no money, no land, n opportunity to gain financially. Tremendous progress I thought represented a lifting of a majority in a populace, not a financial stagnation from a majority that never had financial betterment.
The biggest problem with Black people in the usa, is the lie we tell ourselves about the commonly called Great Migration, which I call the Black fleeing. Black people flew from the south cause black people were being killed/murdered/incarcerated absent criminal activity/assaulted through the entirey of reconstruction, ask Ida B Wells and flew to the northern cities to be treated better. Most black people did not think they were going to financial betterment outside the south. I wonder where that myth comes from. Yes, some black people sought financial betterment but most wanted away from whitey.The firs thing he said that is truth, Black people always flew back to the south. But the reason was always simple. Thew white governments of the exosouth [north or west] was no better than the white governments of the south. Remember, Tulsa, which wasn't majority black like NYC, Chicago, Los ANgeles, had a government that aided in the bombing and looting of the black community in tulsa by the white community. To be blunt, NYC, Chicago, Los ANgeles were not haven cities for blacks, that is a myth. But the fact that they were not is why black people flew back.
Now what is missing. Many years ago, during Obama's first campaign I suggested Black people in the usa needed a black party of governance in the usa to focus on places where the populace of black people is largest. He speaks of Black Power in government locally in the southern states but doesn't suggest a black party of governance in said states? why? I always find it strategically silly that any community is unwilling to support organizations strictly to their benefit when they have numerical advantage.
Why do the black towns and counties of the south have representatives of andrew jackson or abraham lincoln when both have proven to be useless in being effective to making or administering legal policy to Black benefit.I emailed him my thoughts, you can do the same
chblow@nytimes.comSome post where I spoke on this
https://aalbc.com/tc/blogs/entry/194-richard-murray-creative-table/page/5/?tab=comments#comment-496
https://aalbc.com/tc/profile/6477-richardmurray/?status=1945&type=status

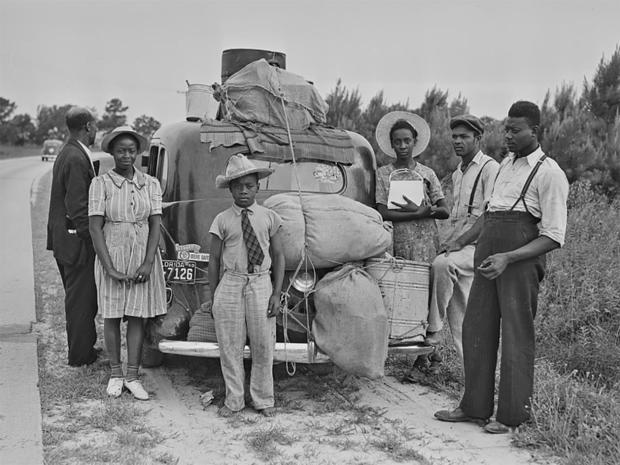
This photo is part of the problem. Most black people didn't own a car. This black family is financially the black one percent. This black family is looking for financial betterment but most black people owned nothing. I know for certain. Most Black people fled the south , walking, taking the train, fleeing white violence. But the narrative whites like to hear, ala magical negro is it was a simple financial move.
Charles M. Blow on reversing the Great Migration
sunday-morning
BY CHARLES M. BLOWDECEMBER 17, 2023 / 10:25 AM EST / CBS NEWS
Our commentary is from New York Times columnist Charles M. Blow, whose new HBO documentary "South to Black Power" is now streaming on Max:At the end of the Civil War, three Southern states (Louisiana, South Carolina and Mississippi) were majority Black, and others were very close to being so. And during Reconstruction, the 14th and 15th Amendments to the Constitution made Black people citizens and gave Black men the right to vote.
This led to years of tremendous progress for Black people, in part because of the political power they could now access and wield on the state level.
But when Reconstruction was allowed to fail and Jim Crow was allowed to rise, that power was stymied. So began more decades of brutal oppression.In the early 1910s, Black people began to flee the South for more economic opportunity and the possibility of more social and political inclusion in cities to the North and West. This became known as the Great Migration, and lasted until 1970.
But nearly as soon as that Great Migration ended, a reverse migration of Black people back to the South began, and that reverse migration – while nowhere near as robust of the original – is still happening today.
In 2001 I published a book called "The Devil You Know," encouraging even more Black people to join this reverse migration and reclaim the state power that Black people had during Reconstruction. I joined that reverse migration myself, moving from Brooklyn to Atlanta.
Last year, I set out to make a documentary which road-tested the idea, traveling the country, both North and South, and having people wrestle with this idea of Black power.
Here are three things I learned from that experience.
First, Black people are tired of marching and appealing for the existing power structure to treat them fairly.
Second, young Black voters respond to a power message more than to a message of fear and guilt.
And third, many of the people I talked to had never truly allowed themselves to consider that there was another path to power that didn't run though other people's remorse, pity, or sense of righteousness.
I don't know if Black people will heed my call and reestablish their majorities, or near-majorities, in Southern states. But sparking the conversation about the revolutionary possibility of doing so could change the entire conversation about power in this country, in the same way that it has changed me.
URL
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/charles-m-blow-on-reversing-the-great-migration-south-to-black-power/Different Tribes of Black people slowly becoming one takes too long to retain gains or start new gains
Alabama
Black Descendent of enslaved leaders guided the majority populace of said people to do what Maher says the palestinean should do. Based on the history of said people my advice is for the palestinean to keep fighting for the river to the sea. Yes, it may lead to a termination of palestineans. But, look at the native american in the usa. Look at the black descended of enslaved in the usa.
Two peoples who in overwhelming majority, not all, chose the path Maher suggest the palestinean choose. What did it lead to?
Whites in the USA got what they wanted, they got to win a blood feud absent having to kill the rivals in the feud, and then use that as a symbol of usa greatness. The black descended of enslaved plus native american became idolters, mostly ranked by people who are completely infatuated to the culture of those who enslaved them, completely impotent populaces concerning what can only come from collective force, beggers or crawlers in the system designed by rivals in a blood feud.
Maher is correct, as someone in this community said to me the same as other black people said many times in earshot in my offline life, the past can not be changed. But, how you plan for the future does not have to suggest the past didn't happen. And that is what Maher truly wants, what the native american of the usa did, what the black descended of the usa did, for the palestinean people to eat the crow of accepting the system of their opposer and embrace said system. Then they can have a palestinean president of israel. They can have dancing jolly musicals about the fiscally poor palestineans abused by the tyrranical israelis hurting each other for relief. They can mate with israelis and have a bunch of loving palestinean-israeli mulattoes. Yeah, I know what Maher is suggesting to the palestinean. If the palestinean is wise,better for the community to die than to become the native american of the usa.Maher on palestineans
Maher on netanyahu
IN AMENDMENT
The problem with netanyahu is like so many , he is unwilling to embrace the truth of his country,this is what hitler did that many leaders are unwilling to do. Embrace the power and violence of their government as power+ violence. The Statian empire teaches all governments that power must always be wielded as benevolence, this comes from the british imperial tradition that create the usa. But I oppose that, if you are a bully be a bully. You want to push the palestineans out, then simply do it. Trying to suggest you are legal or pure or a good person or some other thing to make a false narrative in a history book or to assuade your descendents of how they got their wealth is to me a true sin. Maher says Israel is powerful , well it is time for israel to embrace that position. And to embrace that the zionist chose this location. If the zionist were wise they would had chosen somewhere in europe but they were not, they assumed they could chose a muslim place and convert it through influence of their big brother who was started the same way, the usa. But they underestimated that not all peoples are the native american + black descended of enslaved who are weak peoples. So the zionist made the bed, the israeli has to live in it, israel will always be the enemy of its neighbors, that is the zionist legacy, netanyahu needs to embrace it and kick the palestinean out and live surrounded by enemies.
What DAvid Alan Grier said is correct, and in the situation of candy cane lane holds truth but the reason it isn't industry wide must be discussed. The problem with the narrative is, who owns is irrelevant . Grier says all need to see themselves, and he isn't wrong but black people don't see themselves in media in the usa cause black people don't own the media. Many black people in the usa seem to think not owning sports team, not owning film studios, not owning music labels, not owning car companies, not owning gun manufacturers, not owning cement makers, not owning real estate , not owning mass produce producers[corporate farms], is not a factor. Black people in the usa don't own any industry. That is why Black people are not present as we will like in any industry in the usa. IT is very simple. But the reason black people don't own is because of our history under this government , historically white, that placed us in a negative financial state where whites disallowed us from owning. Yes, starting in the 1980s, it can be said that the black populace in the usa finally was free from the yoke of the whites to grow as individuals BUT it matters when whites in the usa have opportunities to take native american land, when whites have the opportunity to rip natural resources from the earth, when whites have the opportunity to have a gilded age making fortunes for bloodlines off of acts today deemed illegal. MErit isn't unimportant. I am not knocking down merit. But merit isn't more important than opportunity but opportunity in the usa comes from ownership not merit. And ownership in the USA 99% of the time comes from advantage through an ancestor using arms, guns, or inheriting wealth from an ancestor who used arms, guns.
...
This situation reflects my point, ownership is more important than merit or equality. eddie mruphy is an owner/a producer and makes the choices, if eddie murphy didn't put grier or someone black as santa that is his choice. My point is ownership is superior to merit. Black culture/storytelling has always been present to support black people feeling apart of anything. And I know cause growing up as a kid I never felt deprived of black presence in media or in any season cause of my parents.David Alan Grier on Why His Surprise Cameo as Black Santa in ‘Candy Cane Lane’ Reminded Him of ‘Black Panther’
The film reunited him with his 'Boomerang' collaborators Eddie Murphy and director Reginald Hudlin.
BY CHRIS GARDNERPlus Icon
DECEMBER 9, 2023 11:15AMAs the Candy Cane Lane premiere red carpet heated up Nov. 28, two publicist elves worked their way down the press line to remind journalists not to spoil the big reveal from the Reginald Hudlin-directed holiday adventure.
The Prime Video release, penned by Kelly Younger, stars Eddie Murphy as a recently unemployed man on a mission to win his neighborhood’s annual Christmas home decoration contest. The hush-hush surprise happens late in the film when David Alan Grier crash-lands in an ultra-slick sleigh as (the lifted embargo permits us to announce) Black Santa Claus.
“Reggie called and told me what his idea was and I was overjoyed, man. He let me flow and egged me and Eddie on,” explained Grier of reteaming with Hudlin and Murphy with whom he teamed for the 1992 romantic comedy Boomerang. “That was over 30 years ago and all we talked about were cars, clubs, big houses, like ‘Where y’all going tonight.’ This was different because Eddie is so chill. He has kids, grandkids. He seemed really, really happy.”
As far as the significance of playing an iconic character as a Black man, Grier said the opportunity reminded him of Black Panther. “When you see yourself represented in movies or stories, it’s an affirmation that you exist, that you belong, and that you’re legitimate. That’s what people forget about to see ourselves, not just us, everybody. There’s room for all of us at the table. This is the first Christmas movie I ever did so it’s got to last a long time.”
Who knows, there may also be a sequel. Prime Video announced last week that following its debut, Candy Cane Lane quickly became the No. 1 movie worldwide on Prime Video, the most-watched am*zon MGM Studios-produced movie debut ever in the U.S. and among the top 10 worldwide film debuts ever on the service.
“The sensational debut of Eddie Murphy’s first-ever Christmas movie, Candy Cane Lane, is a true demonstration of how joyful, family-oriented stories can touch the hearts of viewers around the world,” offered Courtenay Valenti, head of film, streaming, and theatrical at am*zon MGM Studios.
Grier is also counting his blessings this holiday season. “I’m going to tell you right now, I’m 67 years old. I did not think that my career would be here at my age. I have more work than I can even say yes to. My career is booming and I feel like I finally figured out what I’m doing, so I’m only getting better and better. We’ll see what happens.”
the american society of magical negroes trailer
For centuries, there has been a society hidden in plain sight, working in secret to protect Black people from harm. It’s called THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MAGICAL NEGROES.
A new satire from writer/director Kobii Libi and an official selection of Sundance 2024. Only in theaters March 22.guiliani as mayor of new york made policy intentionally harming the black populace in nyc, that being the selling of nyc properties that black people lived in, properties nyc owned because the real estate industry failed which many forget... is his actions toward two black female poll workers a shock to black new york city dwellers? The answer is no.
kamala harris broke the record on tiebreak votes but is the quality of her tiebreaks showing she is thoughtful or functional?
https://www.blackenterprise.com/kamala-harris-200-year-record-tiebreakers-cast/Question, should black people in the south look to reboot the majority of historical black colleges that went under?
For example the Conroe Normal and Industrial College faculty (c. 1903)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conroe_Normal_and_Industrial_College
referal
Mandela on a Black countries government
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i5TiUhhm7cQor
Please read MEdical Apartheid by Harriet Washington
https://www.kobo.com/us/en/ebook/medical-apartheid
the referral
https://www.msn.com/en-us/health/other/smithsonian-targeted-dc-s-vulnerable-to-build-brain-collection/ar-AA1lukXG
-
A Call for Submissions
for the Killens Review of Arts & Letters
Spring 2024All That We Carry: Where Do We Go From Here?
Deadline: Friday, December 1, 2023
The Killens Review of Arts & Letters is a peer-reviewed journal that welcomes Black writers and artists whose work speaks to the general public and to an intergenerational range of readers represented throughout the African diaspora. For the Spring 2024 issue of the Killens Review, we are seeking short stories, essays, creative nonfiction, poetry, art, and photography. Inspired by questions posed by Dr. Tiya Miles, eminent historian and creative writer, and Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., we are soliciting content that reflects how Black creatives from all parts of the world move forward when all around us is in disarray. Specifically, we ask that you submit original writing or art that explores the themes of legacy, memory, inheritance, and/or radical hope (or pessimism), with an orientation toward the future and future generations of Black peoples.
Application
https://centerforblackliterature.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/CFP_Killens-Review-Spring-2024.pdf
-
We’re back with the Kobo Writing Life Indie Cover Contest, 2023 edition! This is a great chance to show off your best cover of 2023 and vote for your other favourites (or your own – no judgement here!). The four winners, one in each genre category, will receive an amazing suite of prizes: a Kobo Clara 2E, promotional opportunities, and, of course, bragging rights and recognition!
Check out 2021’s winners here! [ https://kobowritinglife.com/2022/01/10/2021-kwl-indie-cover-contest-and-the-winner-is/ ]
There will be two weeks to submit your cover. The submission period starts TODAY, November 1st, and closes at 11:59pm EST on November 17th. Once all submissions have been received, the KWL team will begin the jurying process!
Our expert team of merchandisers and marketers will select six covers from each genre to feature on four shortlists, for a total of 24 shortlisted covers. Voting will then be open to the public, and YOU, the author and reader community, will select the overall winners: one from each genre category of Romance, Mystery, and Sci-fi & Fantasy!
For your cover to be eligible:
Your book must be uploaded directly through Kobo Writing Life
Have a publication date or planned publication date in 2023 (January 1st 2023 – December 31st 2023)
Be categorized in one of the following four genre groups: Romance, General Fiction & Non-fiction, Mystery & Suspense, or Science Fiction & Fantasy
Notes:
This contest is open to titles of all languages.
This contest is open worldwide.
Any sub-genre is eligible for submission.
One entry per author. Authors with multiple pen names are subject to the one entry per author ruling as well, i.e., if you have two pen names, you cannot submit 2 entries; the maximum submission number remains 1 title per individual.
Only winners in certain regions will be able to receive a Kobo Clara 2E as a prize. If you reside in one of the ineligible regions, you will be provided with an alternative prize package.
Any submissions that do not follow the above rules and requirements will not be eligible for participation in the contest.
Rules and regulations subject to change at the behest of the Kobo Writing Life team.
If you have any questions, please contact us at writinglife@kobo.com.
SUBMIT YOUR COVERS HERE! [ https://forms.office.com/r/nTw7KXMccb ]
Important Dates:
SUBMISSION PERIOD: November 1st – 17th at 11:59PM EST
KWL TEAM JURYING PERIOD: November 20th – 24th
SHORTLISTS ANNOUNCED, VOTING BEGINS: November 27th
VOTING PERIOD ENDS: December 15th at 11:59PM EST
WINNERS ANNOUNCED: week of December 18th
URL
https://kobowritinglife.com/2023/11/01/announcing-the-kobo-writing-life-2023-indie-cover-contest/
-

@Milton @Mel Hopkins check this out
-
-
 1
1
-
- Report
-
-
Title: Hovergirls physical version coming
Artist: GDbee < https://gdbee.store/ > aka Prinnay
Prior posthttps://aalbc.com/tc/profile/6477-richardmurray/?status=2490&type=status
GDBee Post
https://aalbc.com/tc/search/?&q=gdbee&type=core_statuses_status&quick=1&author=richardmurray&search_and_or=or&sortby=newestpreorder
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/hovergirls-geneva-bowers/1143848338
her social list
https://gdbee.carrd.co/FROM THE ARTIST
I am SO excited to reveal the cover for the physical version of HoverGirls! It'll be hittin the shelves next summer!
It's basically the webcomic completely redrawn, freshly edited, and with more story! I'm extremely proud of how it came out. The original will always be here but the new edition literally has 100 more pages of story, and 99% less typos
If you love magical girls, struggling slice of life, parodies, and/or struggling slice of life magical girl parodies, you'll love HG, I promise!
*It's being published by Bloomsbury in August 2024* -
The Hemiclitoris of the snake
Scientists finally discovered the snake clitoris, and they're 'very excited'
News
By Joanna Thompson
published December 16, 2022
Megan Folwell stood over a female Australian death adder (Acanthophis antarcticus), armed with a scalpel. The snake was dead, donated by a venom supply company. Very carefully, Folwell, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Adelaide in Australia, made an incision near the animal's tail. She was about to go where no scientists had gone before.
"I went into it not knowing what I was going to see," Folwell told Live Science.
Until now, no one had taken the time to look for and describe a snake's clitoris. With the exception of birds, clitorises are found in every vertebrate lineage, including snakes' closest cousins, lizards. But when Folwell went looking for literature about the organ in serpents, she came up empty-handed. "It just didn't make sense to me," she said. "I knew there had to be something going on."
So she and her team decided to investigate. Their results, published Dec. 14 in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, describe the structure of the forked "hemiclitoris" in snakes for the first time.
In contrast, male snake genitalia have been well documented across a variety of species. Male snakes have a structure called a hemipenis, essentially a two-pronged penis tucked under the base of the tail (and often held inside the body until mating). Much scientific ink has been spilled over the past 200 years describing differences between hemipenes, which range in size and shape from tiny twin toothpicks to huge, elaborate organs with "a lot of spines on them and whatnot," said Richard Shine, an evolutionary biologist at Macquarie University in Australia who was not involved in the study.
Despite more than two centuries' worth of data on hemipenes, however, nobody had described an equivalent structure in female snakes. The lack of evidence caused some scientists to speculate that snake hemiclitorises might not exist at all — or that, if they did, they had been reduced to a stunted evolutionary remnant.
A lack of research around female anatomy is a troubling scientific trend. Even in humans, surprisingly little is known about the clitoris. The full structure of the organ, which includes not only the little nub at the top of the labia but also two large internal bulbs full of nerve endings, wasn't discovered until the mid-1840s. Even then, it remained relatively obscure to the medical establishment until Australian urologist Helen O'Connell's work in 2005, which showed that typical textbook depictions of the clitoris were riddled with inaccuracies. In fact, just last month, scientists counted all 10,000 nerve fibers in the human clitoris for the first time.
Data about female reproductive anatomy and behavior in nonhuman animals are even more scarce. A November analysis published in the journal Nature found that between 1970 and 2021, more than seven times as many papers were published about sperm competition in animals compared with female mate selection. A 2014 perspectives article published in the journal PLOS Biology found that about 50% of all studies of animal genitalia published between 1989 and 2013 focused exclusively on males, while 10% focused only on females.
"If genetal evolution research only investigates the male parts, it gives a very lopsided understanding of nature," Malin Ah-King, an evolutionary biologist and gender researcher at Stockholm University in Sweden who was not involved in the new research, told Live Science. This bias has led scientists to overlook certain important aspects of female reproduction — such as the existence of entire organs.
Thanks to Folwell's efforts, we now know that hemiclitorises exist in at least nine snake species. Folwell carefully dissected preserved specimens from four snake families (Elapidae, Pythonidae, Colubridae and Viperidae) and ran them through a CT (computed tomography) scan, noting the size and shape of each hemiclitoris. She found that they varied as much as hemipenes.
"Seeing the nerve structure, it was really exciting," said Folwell, the study's first author. And in other scientists' defense, she said, the tissue that makes up snakes' hemiclitorises is quite delicate (even though, in some cases, the organ was fairly large).
Shine described the new research as "an excellent piece of work." "It certainly convinces me that there is a structure there," he told Live Science.
For Folwell and her team, this study is merely the start of this research. She hopes that future work will uncover a fuller picture of the hemiclitoris's evolutionary history and how it fits into snake mating behavior. "We're really very excited about all of this," she said.
URL
https://www.livescience.com/snake-clitoris-found
First evidence of hemiclitores in snakes
Megan J. Folwell, Kate L. Sanders, Patricia L. R. Brennan and Jenna M. Crowe-Riddell
Published:14 December 2022https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2022.1702LOOK IN THE FIRST COMMENT FOR THE ABSTRACT
URL
https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rspb.2022.1702
-

Abstract
Female genitalia are conspicuously overlooked in comparison to their male counterparts, limiting our understanding of sexual reproduction across vertebrate lineages. This study is the first complete description of the clitoris (hemiclitores) in female snakes. We describe morphological variation in size and shape (n = 9 species, 4 families) that is potentially comparable to the male intromittent organs in squamate reptiles (hemipenes). Dissection, diffusible iodine contrast-enhanced micro-CT and histology revealed that, unlike lizard hemiclitores, the snake hemiclitores are non-eversible structures. The two individual hemiclitores are separated medially by connective tissue, forming a triangular structure that extends posteriorly. Histology of the hemiclitores in Australian death adders (Acanthophis antarcticus) showed erectile tissue and strands/bundles of nerves, but no spines (as is found in male hemipenes). These histological features suggest the snake hemiclitores have functional significance in mating and definitively show that the hemiclitores are not underdeveloped hemipenes or scent glands, which have been erroneously indicated in other studies. Our discovery supports that hemiclitores have been retained across squamates and provides preliminary evidence of differences in this structure among snake species, which can be used to further understand systematics, reproductive evolution and ecology across squamate reptiles.
1. Introduction
Genitalia are some of the fastest evolving characteristics in amniotes with internal fertilization [1]. In these taxa, comparative studies of genitalia provide insights into the role of sexual selection in speciation and the evolution of reproductive traits [2]. Unfortunately, studies of female genitalia have lagged next to an overwhelming focus on male genitalia across amniotes [1,3,4]. This is despite some evidence that female genitalia, and the clitoris in particular, have a key functional role in reproduction [5–8]. For example, variation in clitoris morphology has been linked to different degrees of sexual arousal that could lead to increased reproductive fitness by enticing females to copulate or forming social bonds. Increasing vaginal lubrication, relaxing the vaginal opening and preparing the reproductive tract to receive sperm are among other potential functions of the clitoris [8–11].
Studies on the male hemipenes in lizards and snakes are extensive (e.g. [12]), and have fundamentally shaped ideas on the shared developmental origins of the phallus in amniotes (e.g. [13]), systematic controversies, sexual conflict (e.g. [14]) and diversity of sexual characteristics within the squamate reptiles (e.g. [14,15]). Similar studies of female hemiclitores are rare, and in fact, it is often assumed that the clitoris is vestigial or lost across lineages of squamates [16]. Even when hemiclitores are described in lizards, these have been hypothesized to provide a stimulatory role for the male during intromission [17], rather than to stimulate the female as is the case in other amniotes [8]. Hemiclitores in lizards are eversible and resemble features of the hemipenes such as the sulcus spermaticus and retractor muscles [17–20].
The apparent lack of a hemiclitores in adult snakes is puzzling because this organ is found in most adult female amniotes with the exception of birds [21,22]. During squamate development, the paired genital buds continue growing to create hemipenes or regress in size to form the hemiclitores [23]. Reports of hemiclitores in adult snakes, however, are either, (i) inappropriate citations of literature that discussed lizards rather than snakes, (ii) different sex genitalia in snakes (e.g. intersex or male hemipenes), (iii) vague descriptions without anatomical references or (iv) confused with adjacent anatomy such as the scent glands (e.g. [24]). Many erroneous reports of hemiclitores actually describe hemipenes from intersex individuals, including Bothrops insularis, which have a remarkably high prevalence of intersex individuals with functional oviducts [25], Bothrops jararaca [26] and Lycodryas maculatus [27]. This confusion may stem from imprecise terminology combined with incomplete examinations of gonad anatomy, as some papers define intersex individuals as ‘females with a hemiclitoris', where the hemiclitores were actually intersex hemipenes, and females as ‘females without a hemiclitoris’ [28,29], while other papers describe intersex individuals as ‘females with hemipenes’ [26,27,30–34]. We reviewed these spurious reports and conflicting descriptions of squamate hemiclitores in [27].
Here, we provide the first macro morphological descriptions of hemiclitores using dissection in seven adult female snakes (Elapidae, Viperidae and Pythonidae) and diffusible iodine contrast-enhanced micro-CT (DiceCT) scanning in three adult female snakes (Elapidae and Colubridae). We selected a focus species, the Australian common death adder (Acanthophis antarcticus), to conduct in-depth morphological descriptions of hemiclitores using a combination of dissection, DiceCT scanning and histology. Using histology, we compared hemiclitores structure in females of this species with conspecific male hemipenes from an adult and juvenile. Using DiceCT scanning, we demonstrate the difference between the hemiclitores and the adjacent scent glands, which have previously been erroneously reported as hemiclitores [24]. Clarifying the difference between hemipenes and hemiclitores clears the path for a more comprehensive understanding of snake hemiclitores anatomy and potential function, as well as improving our understanding of intersex genitalia in squamates.
2. Materials and methods
(a) Specimens and euthanasia
We examined female genitalia in 10 adult specimens, eight frozen and two fresh-fixed females, across nine species: Acanthophis antarcticus, Agkistrodon bilineatus, Bitis arietans, Helicops polylepis, Lampropeltis abnorma, Morelia spilota, Pseudechis colleti, Pseudechis weigeli and Pseudonaja ingrami. We also examined the micro-anatomy of the male genitalia in an adult and a juvenile specimen (Acanthophis antarcticus) (electronic supplementary material, table S1). The adults were wild caught and were sourced from either Venom Supplies Pty. Ltd., private collections, or the University of Michigan Museum of Zoology (UMMZ). The juvenile A. antarcticus was born at Venom Supplies.
Once euthanized via injection of pentobarbitone, the specimens were immediately frozen at −20°C. Adult female, male and juvenile male A. antarcticus specimens were used for histology, and an adult female was used for DiceCT scanning (electronic supplementary material, table S1). The adult females of A. bilineatus, B. arietans, M. spilota, P. colleti, P. weigeli and P. ingrami were used for dissection morphology, and H. polylepis and L. abnorma were used for DiceCT morphology (electronic supplementary material, table S1).
(b) Histology
For the female A. antarcticus, the tail was dissected dorsally to identify the hemiclitoral structure medial to the two scent glands, posterior to the cloaca. The hemiclitores structure and both scent glands were removed from the tail and fixed in 10% buffered formalin. For both males, the inverted hemipenes structures were removed and preserved in 10% buffered formalin.
The excised genitalia from the A. antarcticus histology specimens were processed and stained for paraffin histology. Each sample was sliced longitudinally with a microtome 10 times at 5 µm (first nine slides not stained—45 µm), once at 10 µm, then once again at 5 µm. The slides were stained in haematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Bielschowsky silver and Masson's Trichrome, respectively. The slides were scanned using an Axio Scan.Z1 Automated Slide Scanner (Axioscan, Zeiss, Germany) and the ZEN Blue software version 3.4 (Zeiss Zen blue edition, Zeiss, Germany).
(c) Diffusible iodine contrast-enhanced micro-CT
The tail of the female A. antarcticus was removed with a transverse amputation just above the posterior lip of the cloaca. The tail of the death adder and the two colubrid full snake DiceCT specimens were fixed in 10% buffered formalin, rinsed for 24 h and transferred into 70% ethanol for at least two weeks. The tail and whole-bodied specimens were transferred into 50% ethanol for 48 h, then into 25% ethanol for 48 h before submersing in 1–1.25% Lugol's iodine solution (I2 + KI + H2O) for approximately 14 days, as per the following protocol for DiceCT [35]. Scanning was conducted on the tail prior to and post-staining using a SkyScan-1276 Micro-CT (Zeiss, Germany) at the University of Adelaide (Aluminium 1 mm filter, 10 µm, 90 kV, 200 µA), and on the whole-bodied specimens on a Nikon Metrology XTH 225ST µCT scanner (Xtect, Tring, UK) at the UMMZ. The two-dimensional tomography slices for each scan were reconstructed in Avizo version 9.2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) or Volume Graphics Studio Max version 3.2 (Volume Graphics, Heidelberg, Germany) and the hemiclitores segmented using a thresholding tool. The contrast between soft tissue in the tail was low but the hemiclitores could clearly be defined by comparing its position with the images of the dissection and histology and by demarcations between the hemiclitoris and the two scent glands.
3. Results
(a) Discovery of hemiclitores in colubrid, viperid, pythonid and elapid snakes
In all species, the hemiclitores were clearly identified as two separate and non-eversible structures in the tails of females, posterior to the cloaca and medial or medioventral to the two scent glands (figures 1 and 2). DiceCT and dissection revealed the hemiclitores are separated medially by connective tissue that together forms triangular structures, with some shape variation and significant size variation across species (figures 1 and 2). Unlike lizard hemiclitores, all snake hemiclitores examined lacked spines, sulcus spermaticus and retractor muscles, and could not be everted by manual manipulation. Some hemiclitores were large and conspicuous, occupying most of the anterior tail region that extended dorsally towards the spine (Agkistrodon bilineatus) (figure 1a), whereas others were small and medioventral to the scent gland (Helicops polylepis—figure 1c; Pseudonaja ingrami—figure 1h). The elapids and colubrids presented with the smallest hemiclitores, and the viperids had the most prominent ones (figures 1 and 2). Some elapids, Pseudechis colleti, Pseudonaja ingrami and Pseudechis weigeli, presented with hemiclitores that were thin and laid over the top of the scent glands (ventral position) but still in a central position in the tail, thus, medioventral (figure 1f–h). However, Lampropeltis abnorma (figure 1d), like Acanthophis antarcticus, presented with small hemiclitores that extended deeper towards the spine than in other elapids. Another cryptic feature found in some species, Pseudechis colleti and Pseudechis weigeli, was the presence of detached ‘pockets’ anterior to the hemiclitores, posterior to the cloaca and medial to the scent gland openings (figure 1f,h). These pockets consisted of two empty soft tissue pouches, separated through the centre, with the opening along the posterior cloaca lip and pouch extending posteriorly towards the hemiclitores. There was no protrusion of pouch/pocket into the hemiclitores, thus the pockets were detached from the hemiclitores.

Figure 1. Macroanatomy of the snakes hemiclitores and scent glands in mature female (a,b) viperid, (c,d) colubrid, (e) pythonid and (f–h) elapid snakes (specimen IDs and information in the electronic supplementary material, table S1). (a) Agkistrodon bilineatus. (b) Bitis arietans. (c) Unsegmented DiceCT scan transverse slice of a Helicops polylepis. (d) DiceCT three-dimensional model (left of dotted line) with ventral view of the two-dimensional segmented CT scan (right of dotted line) of a Lampropeltis abnorma. (e) Two dissection images of Morelia spilota specimen. (f) Two dissection photos of Pseudechis colleti specimen, undisrupted gross anatomy of the hemiclitores (left of dotted line) and hemiclitores moved to the side to show the scent gland (right of dotted line). (g) Pseudechis weigeli. (h) Pseudonaja ingrami. Dotted lines separate two images that are from the same specimen but a different view. CL: cloaca; H or HC: hemiclitores; M: muscle; P: pockets; SG: scent glands; SGD: scent gland duct. (Online version in colour.)

Figure 2. Macroanatomy of two mature female common death adders (Acanthophis antarcticus) hemiclitores and scent glands (specimen IDs and information in the electronic supplementary material, table S1). (a) Female death adder ‘AA99’ specimen image. (b) Ventral view of a DiceCT three-dimensional model of female specimen ‘AA79’ with and dissection of female specimen ‘AA99’. (c,d) Two ventral view two-dimensional longitudinal slices from a DiceCT scan of a female specimen ‘AA79’ tail (blue line = slice position). (e) Transverse two-dimensional DiceCT slice of female specimen ‘AA79’. CL: cloaca; HC: hemiclitores; SG: scent glands. Death adder image credit: Luke Allen.
(b) Intraspecific comparison of genital micro-anatomy in Acanthophis antarcticus
The hemiclitores were clearly identified in the tails of two female death adders, posterior to the cloaca and medial to the two scent glands (figure 2). DiceCT, dissection and histology revealed the hemiclitores as two independent structures, separated through the midline by connective tissue, that together form a triangular shape extending and tapering posteriorly (figures 2 and 3). The hemiclitores were prominent although small (figure 2; electronic supplementary material, table S1) and extended dorsally towards the spine. Like all other species examined, the hemiclitores lacked spines, sulcus spermaticus and retractor muscles, and could not be manually everted, unlike the adult and juvenile male death adders' hemipenes (electronic supplementary material, figure S1). Dissection and histology of female A. antarcticus revealed that each hemiclitoris had extensive erectile tissue that contained clusters of nucleated red blood cells in the numerous vascular spaces interwoven with collagen, which were identified by H&E and Trichrome stains (figure 3a,c). By contrast, the erectile tissue of the hemipenis had dense muscle fibres alongside but separate from collagen (electronic supplementary material, figure S1). Nerve bundles and single nerve strands were also present throughout the hemiclitores and hemipenes, as seen in the Bielschowsky silver stain (figure 3b; electronic supplementary material, figure S1b,e). The presence of erectile bodies with blood cells suggests that the hemiclitores engorge with blood, while the presence of abundant nerve bundles suggests that their stimulation may provide sensory feedback to the females.

Figure 3. Histology of the hemiclitores and scent glands from mature female death adder specimen ‘AA99’ with (a) hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), (b) Bielschowsky and (c) Masson's trichrome stains. Inset images: (a) red blood cells in the right hemiclitoris and muscle layer between the hemiclitores and cloaca; (b) nerves within the right hemiclitoris; (c) red blood cells and collagen within the right hemiclitoris.
 collagen; CL: cloaca; HC: hemiclitores; M: muscle cells; N: nerve fibres; NB: nucleated red blood cells; SG: scent glands. (Online version in colour.)
collagen; CL: cloaca; HC: hemiclitores; M: muscle cells; N: nerve fibres; NB: nucleated red blood cells; SG: scent glands. (Online version in colour.)
(c) Differentiating the hemiclitores and scent glands
To clear up the misidentification of scent glands with hemiclitores, i.e. [24], we investigated the DiceCT scan of Lampropeltis abnorma (figure 1d) and A. antarcticus (figure 2), and dissected a mature female Morelia spilota (figure 1e), which was one of the species used in [24]. We confirmed that the ‘ovoid structures cranial to the scent gland’ described by [24] were actually part of the scent gland because they clearly connect to the gland and extend to the cloacal opening (figures 1–3). Depending on where the tail was sliced longitudinally, it appeared as if the scent gland and duct were disconnected posteriorly, leading to misidentification of two individual ‘hemiclitores’ located posterior to the scent glands (figure 2). We confirmed that the structures labelled as ‘hemiclitores’ in [24] were actually ducts, by dissecting the tail in M. spilota and using a semi-blunt probe, we found the duct opening at the cloaca (figure 1e). This arrangement of hemiclitores medial to the scent gland and ducts was consistent across the females of the species examined (figures 1 and 2).
4. Discussion
Female genitalia are historically under-studied compared to males [3,4], and this neglect has delayed our understanding of reproductive biology and behaviour of females in nature. Even though the clitoris is present in most female amniotes [1], and as we demonstrate here, in snakes as well, very little is known about the possible functional role and evolution of the hemiclitores in squamates. Here, we report that the hemiclitores in snakes are diverse across a range of species and likely functional. These findings may help us broadly re-examine female choice in snakes via genital stimulation.
(a) Evolutionary significance of snake hemiclitores
Our discovery of hemiclitores in snakes is timely in the field of reproductive biology given the recent enthusiasm for using innovative imaging techniques for explore female anatomy [1] and confusion surrounding the anatomy of hemipenes/hemiclitores in intersex snakes, which is stymieing progress in the field [36]. Quantifying morphological variation in hemiclitores among squamates will be important for understanding mating strategies and testing hypotheses of genital coevolution. The phenotypic diversity of hemiclitores is evident within and between families of snakes and lizards [36] and suggests that courtship and mating differences may have influenced the evolution of hemiclitores morphology. A future comparative study including more reproductively diverse species would help to elucidate the potential role(s) of the squamate hemiclitores.
Our discovery of well-developed, non-eversible hemiclitores in female adult snakes has previously not been accurately described and provides supporting evidence that hemiclitores have been retained across squamates. Several important differences between the male and female genitalia, and notable diversity of hemiclitores across species, challenge previous statements that squamate hemiclitores are a vestigial form of hemipenes, or an intersex hemipene [16], reviewed in [36]. The interspecific diversity of snake hemiclitores parallels that of the male hemipenes [37,38], suggesting that similar selection pressures may influence the shape, size and characteristics, such as detached pockets (figure 1f,g), of the hemiclitores. Further descriptions of hemiclitores, the vagina and conspecific male hemipenes morphology across snake species with different reproductive strategies will be important for mapping the full phenotypic variation and understanding genital evolution in squamate reptiles [1]. Moreover, variation in hemiclitores morphology presents new taxonomic characteristics that may prove useful for resolving the origin of snakes within other squamates (reviewed in [37,38]).
(b) Functional significance of snake hemiclitores
To establish potential function of the hemiclitores, we look at diversity across species, where variation could indicate the action of selection. We investigated variation in gross hemiclitores morphology across clades spanning 100 Myr of snake evolution and found variation across pythonids, colubrids and viperids, and even variation among closely related elapids. The viperid and colubrid species presented with similar interspecific hemiclitores shape and size within each family (figure 1a–d), whereas elapids presented with significant interspecific variation in size, shape and characteristics such as detached pockets (figure 1f–h and figure 2). Characteristics, such as soft tissue detached pockets in Pseudechis, indicate that there are species groupings that may be comparable to taxonomic groupings based on hemipenis morphology and ornamentation, such as spines and hooks, and should be investigated. Additionally, these pockets might represent the ‘mere shallow invaginations' referenced in early descriptions of female squamate genitalia [39]. Unlike ‘pockets’ previously described from inverted intersex hemipenes in snakes [40], these pockets are not the result of inverted genital structures, but rather a pouch of soft tissue detached from the hemiclitores. The presence/absence of these pockets may aid in external access for the males to the anterior section of the hemiclitores in some species, but the function of this structure should be investigated further.
While hemipenes and hemiclitores in snakes share the same developmental pathways during embryogenesis [23,36], our histological comparison of these structures in A. antarcticus identified several anatomical differences between them (figure 3; electronic supplementary material, figure S1). The snake hemiclitores are composed of collagen and vascularized spaces (erectile tissue), connective tissue and dense innervation, but lack muscle fibres in the erectile tissue, and other hemipenis characteristics, such as spines. Since hemipenis spines and muscle fibres in the erectile tissue are present in both juvenile and adult males (electronic supplementary material, figure S1), it is unlikely that we missed their presence in our sample of females due to sexual immaturity or an early stage of genital development. Muscle fibres within the hemipenes provide structural support for inflation during hemipenile eversion, and the retractor muscles attached to the hemipenes allow retraction of the hemipenes back into the tail (electronic supplementary material, figure S1) [8]. A lack of these structures in the hemiclitores supports the observation that the hemiclitores are non-eversible in snakes, unlike hemiclitores in lizards [17–20]. Additionally, the hemiclitores are composed of erectile tissue that is likely to swell but not evert (e.g. [8]). Lizard hemipenes and hemiclitores both have muscle fibres and spines, and while these features are often present in snake hemipenes, they are absent in all the hemiclitores examined.
The presence of nerve bundles and single nerve fibres in the hemiclitores may be indicative of tactile sensitivity, similar to the mammalian clitoris [8]. The innervation and erectile tissue of the hemiclitores, and their position close to the posterior lip of the cloaca where the skin is thinner, could allow stimulation during mating through copulatory behaviours, such as tail wrapping and dorsal body looping [8,12,17–20]. These male mating behaviours could provide female sensory stimulation that may elicit female receptivity. The presence of erectile tissue with some evident blood cells suggests that the hemiclitores may have the ability to engorge with blood if stimulated, much like what has been observed in mammals (e.g. [10]), and other amniotes during sexual activity (e.g. [5]). However, the neurophysiology and density of these nerves in snake hemiclitores needs further investigation with more comprehensive histology/immunohistology and behavioural studies to determine whether they have a copulatory purpose [20].
(c) Intersex hemiclitores or intersex hemipenes?
The literature on hemiclitores in snakes has suffered from either misinterpretation or misidentification with intersex genital anatomy [25–29,36,41]. Our anatomical description of hemiclitores in female snakes show that the ‘intersex hemiclitores' from previous studies are more accurately termed as ‘intersex hemipenes’. This is because early reports of intersexuality in snakes describe this condition as the presence of internal female characteristics (i.e. oviducts) alongside genitalia that are paired eversible uni- or bilobed structures with a sulcus spermaticus through the midline and retractor muscles [17,25,42]. Thus, intersex genitalia more closely resemble male hemipenes, albeit they are often a smaller size with minimal spine development. To our knowledge, intersex hemiclitores (accompanied by typical male gonads) have not previously been described. However, it is possible that intersex individuals with typical male gonads and hemiclitores exist, but their genitalia were not fully examined or are confused with small hemipenes. For example, Hoge [25] mentions that four Bothrops insularis embryos had testes with no hemipenes; however, the potential of intersex non-eversible hemiclitores was not investigated. Our description of hemiclitores morphology will allow future studies to properly assign genital characteristics of the hemiclitores and the hemipenes in squamates, which can result in better investigation of the prevalence of intersexual variation. Properly classifying intersex individuals according to whether they have testes and hemiclitores, or ovaries and hemipenes, would be the first step to potentially investigating the mechanisms that make intersex common in snakes.
5. Conclusion
Our study opens fruitful avenues for research into genital development, function and evolution. Our discovery of likely functional snake hemiclitores implies greater morphological diversity of genitalia within squamates than previously described, from the evertable lizard hemiclitores and squamate hemipenes to the non-eversible snake hemiclitores. Variation in the snake hemiclitores might prove to be correlated with courtship and mating behaviours and help us understand female choice. We suggest that the hemiclitores transduce sensation to the female snake during courtship and copulation, which might promote longer and more frequent mating leading to increased fertilization success. Further investigation into the sensory features of snake hemiclitores and hemipenes are needed to determine potential tactile sensitivity. Comparative morphological investigations of hemiclitores and hemipenes within and among taxa would also provide insight into the possible coevolution of male and female genitalia.
Ethics
All specimens were ethically euthanized, and all interactions with animals and collection of samples were conducted under the requirements of the Department for Environment and Water and the institutional guidelines of Venom Supplies Pty. Ltd and were undertaken in conformance with the Animal Welfare Act 1985 (South Australia).
Data accessibility
The datasets supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the supplementary material and online from the Dryad Digital Respository: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.j6q573nh3 [43].
The data are provided in the electronic supplementary material [44].
Authors' contributions
M.J.F.: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing—original draft and writing—review and editing; K.L.S.: investigation, project administration, supervision, validation and writing—review and editing; P.L.R.B.: investigation, project administration, validation and writing—review and editing; J.M.C.-R.: data curation, investigation, methodology, supervision, validation, visualization and writing—review and editing.
All authors gave final approval for publication and agreed to be held accountable for the work performed therein.
Conflict of interest declaration
We declare we have no competing interests.
Funding
Funding was provided by the University of Adelaide student support fund to M.J.F. and an NSF CAREER grant to P.L.R.B. (grant no. 2042260).
Acknowledgements
For access to specimens, we would like to thank Nathan Dunstan, Luke Allen and the staff from Venom Supplies Pty Ltd, Tanunda, Ralph Foster (South Australian Museum) and Ramon Nagesan, Greg Schneider, Alison Davis Rabosky and José Martínez Fonseca (University of Michigan Museum of Zoology). For microscopy and scanning support, we thank Alessandro Palci and the staff at Adelaide Microscopy and Adelaide Medical School.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material is available online at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.c.6316560.
© 2022 The Authors.Published by the Royal Society under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, which permits unrestricted use, provided the original author and source are credited.
-
-
IS SCHRUMPFT A LEADER
I don't consider schrumpt a leader,
but I have a why. He doesn't organize. The maga crowd was the tea party crowd, was the christian conservative crowd in the 1970's-1980s , was the white folk who hanged black folk and burned black folk in the 1960s and before.
Schrumpf didn't get the MAga's angry, they have been ready to fight since the 1950s,since the war between thes tates, since the usa was founded... what Schrumpf did was mob guide, not start , not lead, mob guide, ala the film intruder, take a look, for free:) linked at the end of my comment.
And to get into the black community in the usa, black statians , unlike the white community in the usa, white statians where various whites guide white people with violent intent, black people with violent intent rarely have such a public guide. I know most white media and some black media today talks about people like Nat Turner, and Saint Garvey and Brother Malcolm or lessers like farrakhan or mumia but none of them, to be fair, ever said, just go out and hurt white people. Lock her up, that kind of talk was never uttered by the people i mentioned. The people i mentioned said defend yourself by any means and white media and to be fair, many in black media, take that as equivalent to people like schrumpf in the white community in the usa, with his opeds on five black children.
Leaders can motivate but the problem in the usa is people, black or non black, tend to view the supporters to schrumpft as needing him, they don't need him to be motivated, to be passionate, to be organized, they need him to guide.
This is why so many whites , immigrants, were so appalled by Schrumpt as president, while the maga were happy. it was his executive shift. What if the USA stopped being the policeman of europe. What if the USA joined with Russia against china. What if the USA stopped being the center of the global human migratory storm. For rural whites in the usa this is ideal. now for white city folk , many of whom are from immigrant stock as well as the hordes of non white immigrants, this is the nightmare. SCrumpft is not a legislator or organizer, sequentially his policies couldn't get through congress but as an executive, he put in place the seeds of that and again it was guiding, not leadership.
IF you can not organize, which schrumpft has proven he can not then...in my eyes , you can not be a leader
https://aalbc.com/tc/profile/6477-richardmurray/?status=2422&type=status
-

in the forum post
a person can be well known or popular and be a leader.
I oppose your assertion that schrumpf is a leader, i consider him a mob guide, that goes back to his central park 5 opinion. it didn't lead, scrumpft comprehends a simple truth, the usa is a multiracial country which means a populace in every race in the usa: women/white/black/native/men/young/old/immigrant/christian/muslim/chinese/nigeiran/russian/any other you can think of dislike/hate everybody else. And the populace inside the white community in the usa that dislike/hate everybody else is large enough to be profitable in one way or another.
The proof is the black followers, people say it is shocking but it isn't. The black community in the usa don't have anyone like Schrumpf. a black person , financially safe that can or desires to mouthpiece pure dislike or hate with an anti immigratory or anti integrated position.
Take a look at the film, the intruder, for free
https://aalbc.com/tc/profile/6477-richardmurray/?status=2422&type=status
-
-
Week 4 of the workshop with Betts on Tumblr
Ma'am
based on Girl from Jamaica Kincaid
https://richardmurrayhumblr.tumblr.com/post/728165222399000576/narrative-writing-workshop-with-betts-week4
The First Mass Of The Perihelion At Saint Lamma
https://www.deviantart.com/hddeviant/art/Title-The-First-Mass-Of-The-Perihelion-At-Saint-La-981961141Training Ground
https://rmfantasysetpieces1.tumblr.com/post/728165870205009920/training-groundComplete writing workshop with Betts posts
https://richardmurrayhumblr.tumblr.com/tagged/tumblr writing workshop with bettsCompanion Deviantart folder
https://www.deviantart.com/hddeviant/gallery/88882719/tumblr-writing-workshop-with-bettsficThe soccer blog workshop posts- for it I didn't do all the weeks
https://rmfantasysetpieces1.tumblr.com/tagged/tumblr writing workshop with bettsAfter discussion side a fellow artist. I made a father to son , son to father reflection of girl from Jamaica Kincaid
Title: Boy
Get up and dig a new latrine hole; Get up and clean the tide off the boat; Get up and get the thrush from the field; Get up and clean the hotel's lawn; Get up and search for crabs; Get up gather and remove the hotel's trash; Get up and clean the hotel floor; always work with your head down; always go where Mr. White tells you to; never steal Mr. White's sugar; use your shirt to wrap the cane if no more cloth; when carrying fish don't trip up or no one will want you to carry their fish again; It is best to sweep the hotel at night when the customers are sleep; Is it true you fought in Sunday school?; don't sing songs on the road, people will not hire you; on Sundays act like a good man and be quiet and not the bums you learned those songs from; Don't fight in Sunday school; you musn't speak to those village girls, not even to give directions; don't eat in the street- people will think you are a bum; but I only fight the teacher on Sundays and always after class; this is how to make a reel; this is how to make a hook for the reel; this is how to fish so you will not be a bum singing all over the place; this is how to you repair the roof of my house; this is how you repair the wall of my house; this is how you throw a net; this is how you reel in a net; this is how you clean out a net; remember never smile when you accept a delivery; remember never smile when you complete a delivery; remember never to smile when you confirm a delivery; never sing at any time during a delivery or people will think your a bum; don't sing with that voice or people may think your a girl; don't hang around in groups - a good worker never has time for partying; don't touch people's cars, you might dirty them; don't throw stones at blackbirds, because it might not be a blackbird at all; you have to start fishing in the morning; you have to keep fishing in the afternoon; you have to stay fishing at night; if you don't feel good , keep fishing; only sleep with dem village girls at midnight; never trust dem village girls , never say their kid is yours; if the kid is yours , teach it what i taught you; this is how to spit up in the air if you feel like it, and this is how to move quick so that it doens't fall on you; always spend your money cause you can't save it anywhere; always squeeze bread to make sure it's fresh; but what if the baker won't let me feel the bread?; you mean to say that after all you are really going to be the kind of man who the baker won't let near the bread?
Title: Sir
Why do mornings stink? why are mornings salty? Why do mornings cut my feet? Why do mornings make me cough? Why do mornings make me tired? Why do mornings never have breakfast? Why do mornings make my skin bleach? Can I look up at a white cloud? Is Mr. White your father? Why can't Mr. White cut his own sugar? Why didn't you tell me the cane can cut my skin? Why didn't you ever help me carry fish? Why couldn't you ever help me sweep the hotel? Papa never helped you to. Why you hit me whenever I was happy. Why does nobody smile at church? Why do we live in homes like the village people? why does no one have anything to eat ? My father loved me like I love you, the best love is the love you don't know. why didn't you go out to sea with me? why didn't you fish with me? Why didn't you ever smile when you caught fish, or show off fish? Why do you always grunt to Mama? Why don't you ever smile to Mama? Why didn't you throw a net with me? Why didn't you reel a net with me? Why didn't you clean out a net with me? Why can't I want to do what I do? Why can't I like what I do? Why can't I love what I do? Why can't I tell people I am happy? Why do people think I am a girl if I am happy? Why don't you have any friends? Why can't I have a morning off? Why can't I have an afternoon off? Why can't I have an evening off? Why do you not sleep at home at night? Why do you never trust what mama say? Why is all your money spent on rum? Why did you never let me squeeze bread around you? I don't need your help. So after telling me what do to all the time, you never cared what I did?
URL
https://richardmurrayhumblr.tumblr.com/post/728754332023029760/boy-and-sir
-
The only government that has global reach is the usa. so what is afria's role in the usa'a scheme.
The USA, like all empires before it and after, fears every other government.
All the governments in Africa have a high level of impotence, but it isn't from a one size fits all narrative. The reality is, from a solely African lens, modernity, circa 2023, is merely a continuation of the european imperial age. The only difference is the usa is in the place of western europe.
As a region Africa joins LAtin America, joins Southern ASia, as regions where the USA doesn't have any militaristic rivals< usa/china > or satraps< germany/japan>. Merely a collection of weak governments whose allegiance is always wanted by the usa but whose impotency or dysfunction makes them unable to be rivals or satraps.
Now things do change, that must be said. But I can't see the future, to say when/how/why.
Original question
#Africa, a continent of 54 countries and a population of about one billion people, accounts for just 3% of global GDP and global trade. How important is #Africa in the #global scheme of things? Discuss…
https://twitter.com/osasuo/status/1700500796813529458

-
Pokemon Rainforest
I put a Sudowoodo in there
colored
https://www.deviantart.com/hddeviant/art/Sudowoodo-in-the-rainforest-Color-981132583
coloring page
https://www.deviantart.com/hddeviant/art/Sudowoodo-in-the-rainforest-BW-981132421
-
The Intruder 1962
Directed by Roger Corman
Written by Charles Beaumont
Starring William Shatner
The Beautiful People
By Charles Beaumont


Mary was a misfit.
She didn't want to be beautiful. And she wasted time doing mad things—like eating and sleeping.
The Beautiful People
By Charles Beaumont
MARY sat quietly and watched the handsome man's legs blown off; watched further as the great ship began to crumple and break into small pieces in the middle of the blazing night. She fidgeted slightly as the men and the parts of the men came floating dreamily through the wreckage out into the awful silence. And when the meteorite shower came upon the men, gouging holes through everything, tearing flesh and ripping bones, Mary closed her eyes.
"Mother."
Mrs. Cuberle glanced up from her magazine.
"Hmm?"
"Do we have to wait much longer?"
"I don't think so. Why?"
Mary said nothing but looked at the moving wall.
"Oh, that." Mrs. Cuberle laughed[6] and shook her head. "That tired old thing. Read a magazine, Mary, like I'm doing. We've all seen that a million times."
"Does it have to be on, Mother?"
"Well, nobody seems to be watching. I don't think the doctor would mind if I switched it off."
Mrs. Cuberle rose from the couch and walked to the wall. She depressed a little button and the life went from the wall, flickering and glowing.
Mary opened her eyes.
"Honestly," Mrs. Cuberle said to a woman sitting beside her, "you'd think they'd try to get something else. We might as well go to the museum and watch the first landing on Mars. The Mayoraka Disaster—really!"
The woman replied without distracting her eyes from the magazine page. "It's the doctor's idea. Psychological."
Mrs. Cuberle opened her mouth and moved her head up and down knowingly.
"Ohhh. I should have known there was some reason. Still, who watches it?"
"The children do. Makes them think, makes them grateful or something."
"Ohhh."
"Psychological."
Mary picked up a magazine and leafed through the pages. All photographs, of women and men. Women like Mother and like the others in the room; slender, tanned, shapely, beautiful women; and men with large muscles and shiny hair. Women and men, all looking alike, all perfect and beautiful. She folded the magazine and wondered how to answer the questions that would be asked.
"Mother—"
"Gracious, what is it now! Can't you sit still for a minute?"
"But we've been here three hours."
Mrs. Cuberle sniffed.
"Do—do I really have to?"
"Now don't be silly, Mary. After those terrible things you told me, of course you do."
An olive-skinned woman in a transparent white uniform came into the reception room.
"Cuberle. Mrs. Zena Cuberle?"
"Yes."
"Doctor will see you now."
Mrs. Cuberle took Mary's hand and they walked behind the nurse down a long corridor.
A man who seemed in his middle twenties looked up from a desk. He smiled and gestured toward two adjoining chairs.
"Well—well."
"Doctor Hortel, I—"
THE doctor snapped his fingers.
"Of course, I know. Your daughter. Ha ha, I certainly do know your trouble. Get so many of them nowadays—takes up most of my time."
"You do?" asked Mrs. Cuberle. "Frankly, it had begun to upset me."
"Upset? Hmm. Not good. Not good at all. Ah, but then—if people did not get upset, we psychiatrists would be out of a job, eh? Go the way of the early M. D. But, I assure you, I need hear no more." He turned his handsome face to Mary.[7] "Little girl, how old are you?"
"Eighteen, sir."
"Oh, a real bit of impatience. It's just about time, of course. What might your name be?"
"Mary."
"Charming! And so unusual. Well now, Mary, may I say that I understand your problem—understand it thoroughly?"
Mrs. Cuberle smiled and smoothed the sequins on her blouse.
"Madam, you have no idea how many there are these days. Sometimes it preys on their minds so that it affects them physically, even mentally. Makes them act strange, say peculiar, unexpected things. One little girl I recall was so distraught she did nothing but brood all day long. Can you imagine!"
"That's what Mary does. When she finally told me, doctor, I thought she had gone—you know."
"That bad, eh? Afraid we'll have to start a re-education program, very soon, or they'll all be like this. I believe I'll suggest it to the senator day after tomorrow."
"I don't quite understand, doctor."
"Simply, Mrs. Cuberle, that the children have got to be thoroughly instructed. Thoroughly. Too much is taken for granted and childish minds somehow refuse to accept things without definite reason. Children have become far too intellectual, which, as I trust I needn't remind you, is a dangerous thing."
"Yes, but what has this to do with—"
"With Mary? Everything, of course. Mary, like half the sixteen, seventeen and eighteen year olds today, has begun to feel acutely self-conscious. She feels that her body has developed sufficiently for the Transformation—which of course it has not, not quite yet—and she cannot understand the complex reasons that compel her to wait until some future date. Mary looks at you, at the women all about her, at the pictures, and then she looks into a mirror. From pure perfection of body, face, limbs, pigmentation, carriage, stance, from simon-pure perfection, if I may be allowed the expression, she sees herself and is horrified. Isn't that so, my dear child? Of course—of course. She asks herself, why must I be hideous, unbalanced, oversize, undersize, full of revolting skin eruptions, badly schemed organically? In short, Mary is tired of being a monster and is overly anxious to achieve what almost everyone else has already achieved."
"But—" said Mrs. Cuberle.
"This much you understand, doubtless. Now, Mary, what you object to is that our society offers you, and the others like you, no convincing logic on the side of waiting until age nineteen. It is all taken for granted, and you want to know why! It is that simple. A non-technical explanation will not suffice—mercy no! The modern child wants facts, solid technical data, to satisfy her every question. And that, as you can both see, will take a good deal of reorganizing."
"But—" said Mary.
"The child is upset, nervous, tense; she acts strange, peculiar, odd, worries you and makes herself ill because it is beyond our meagre powers to put it across. I tell you, what we need is a whole new basis for learning. And, that will take[8] doing. It will take doing, Mrs. Cuberle. Now, don't you worry about Mary, and don't you worry, child. I'll prescribe some pills and—"
"No, no, doctor! You're all mixed up," cried Mrs. Cuberle.
"I beg your pardon, Madam?"
"What I mean is, you've got it wrong. Tell him, Mary, tell the doctor what you told me."
Mary shifted uneasily in the chair.
"It's that—I don't want it."
The doctor's well-proportioned jaw dropped.
"Would you please repeat that?"
"I said, I don't want the Transformation."
"D—Don't want it?"
"You see? She told me. That's why I came to you."
The doctor looked at Mary suspiciously.
"But that's impossible! I have never heard of such a thing. Little girl, you are playing a joke!"
Mary nodded negatively.
"See, doctor. What can it be?" Mrs. Cuberle rose and began to pace.
THE DOCTOR clucked his tongue and took from a small cupboard a black box covered with buttons and dials and wire.
"Oh no, you don't think—I mean, could it?"
"We shall soon see." The doctor revolved a number of dials and studied the single bulb in the center of the box. It did not flicker. He removed handles from Mary's head.
"Dear me," the doctor said, "dear me. Your daughter is perfectly sane, Mrs. Cuberle."
"Well, then what is it?"
"Perhaps she is lying. We haven't completely eliminated that factor as yet; it slips into certain organisms."
More tests. More machines and more negative results.
Mary pushed her foot in a circle on the floor. When the doctor put his hands to her shoulders, she looked up pleasantly.
"Little girl," said the handsome man, "do you actually mean to tell us that you prefer that body?"
"Yes sir."
"May I ask why."
"I like it. It's—hard to explain, but it's me and that's what I like. Not the looks, maybe, but the me."
"You can look in the mirror and see yourself, then look at—well, at your mother and be content?"
"Yes, sir." Mary thought of her reasons; fuzzy, vague, but very definitely there. Maybe she had said the reason. No. Only a part of it.
"Mrs. Cuberle," the doctor said, "I suggest that your husband have a long talk with Mary."
"My husband is dead. That affair near Ganymede, I believe. Something like that."
"Oh, splendid. Rocket man, eh? Very interesting organisms. Something always seems to happen to rocket men, in one way or another. But—I suppose we should do something." The doctor scratched his jaw. "When did she first start talking this way," he asked.
"Oh, for quite some time. I used to think it was because she was such a baby. But lately, the time getting so close and all, I thought I'd better see you."
"Of course, yes, very wise. Er—does she also do odd things?"[9]
"Well, I found her on the second level one night. She was lying on the floor and when I asked her what she was doing, she said she was trying to sleep."
Mary flinched. She was sorry, in a way, that Mother had found that out.
"To—did you say 'sleep'?"
"That's right."
"Now where could she have picked that up?"
"No idea."
"Mary, don't you know that nobody sleeps anymore? That we have an infinitely greater life-span than our poor ancestors now that the wasteful state of unconsciousness has been conquered? Child, have you actually slept? No one knows how anymore."
"No sir, but I almost did."
The doctor sighed. "But, it's unheard of! How could you begin to try to do something people have forgotten entirely about?"
"The way it was described in the book, it sounded nice, that's all." Mary was feeling very uncomfortable now. Home and no talking man in a foolish white gown....
"Book, book? Are there books at your Unit, Madam?"
"There could be—I haven't cleaned up in a while."
"That is certainly peculiar. I haven't seen a book for years. Not since '17."
Mary began to fidget and stare nervously about.
"But with the tapes, why should you try and read books—where did you get them?"
"Daddy did. He got them from his father and so did Grandpa. He said they're better than the tapes and he was right."
Mrs. Cuberle flushed.
"My husband was a little strange, Doctor Hortel. He kept those things despite everything I said.
"Dear me, I—excuse me."
The muscular, black-haired doctor walked to another cabinet and selected from the shelf a bottle. From the bottle he took two large pills and swallowed them.
"Sleep—books—doesn't want the Transformation—Mrs. Cuberle, my dear good woman, this is grave. Doesn't want the Transformation. I would appreciate it if you would change psychiatrists: I am very busy and, uh, this is somewhat specialized. I suggest Centraldome. Many fine doctors there. Goodbye."
The doctor turned and sat down in a large chair and folded his hands. Mary watched him and wondered why the simple statements should have so changed things. But the doctor did not move from the chair.
"Well!" said Mrs. Cuberle and walked quickly from the room.
The man's legs were being blown off again as they left the reception room.
MARY considered the reflection in the mirrored wall. She sat on the floor and looked at different angles of herself: profile, full-face, full length, naked, clothed. Then she took up the magazine and studied it. She sighed.
"Mirror, mirror on the wall—" The words came haltingly to her mind and from her lips. She hadn't read them, she recalled. Daddy had said them, quoted them as he put it.[10] But they too were lines from a book—"who is the fairest of—"
A picture of Mother sat upon the dresser and Mary considered this now. Looked for a long time at the slender, feminine neck. The golden skin, smooth and without blemish, without wrinkles and without age. The dark brown eyes and the thin tapers of eyebrows, the long black lashes, set evenly, so that each half of the face corresponded precisely. The half-parted-mouth, a violet tint against the gold, the white, white teeth, even, sparkling.
Mother. Beautiful, Transformed Mother. And back again to the mirror.
"—of them all...."
The image of a rather chubby girl, without lines of rhythm or grace, without perfection. Splotchy skin full of little holes, puffs in the cheeks, red eruptions on the forehead. Perspiration, shapeless hair flowing onto shapeless shoulders down a shapeless body. Like all of them, before the Transformation.
Did they all look like this, before? Did Mother, even?
Mary thought hard, trying to remember exactly what Daddy and Grandpa had said, why they said the Transformation was a bad thing, and why she believed and agreed with them so strongly. It made little sense, but they were right. They were right! And one day, she would understand completely.
Mrs. Cuberle slammed the door angrily and Mary jumped to her feet. She hadn't forgotten about it. "The way you upset Dr. Hortel. He won't even see me anymore, and these traumas are getting horrible. I'll have to get that awful Dr. Wagoner."
"Sorry—"
Mrs. Cuberle sat on the couch and crossed her legs carefully.
"What in the world were you doing on the floor?"
"Trying to sleep."
"Now, I won't hear of it! You've got to stop it! You know you're not insane. Why should you want to do such a silly thing?"
"The books. And Daddy told me about it."
"And you mustn't read those terrible things."
"Why—is there a law against them?"
"Well, no, but people tired of books when the tapes came in. You know that. The house is full of tapes; anything you want."
Mary stuck out her lower lip.
"They're no fun. All about the Wars and the colonizations."
"And I suppose books are fun?"
"Yes. They are."
"And that's where you got this idiotic notion that you don't want the Transformation, isn't it? Of course it is. Well, we'll see to that!"
MRS. CUBERLE rose quickly and took the books from the corner and from the closet and filled her arms with them. She looked everywhere in the room and gathered the old rotten volumes.
These she carried from the room and threw into the elevator. A button guided the doors shut.
"I thought you'd do that," Mary said. "That's why I hid most of the good ones. Where you'll never find them."
Mrs. Cuberle put a satin handkerchief[11] to her eyes and began to weep.
"Just look at you. Look. I don't know what I ever did to deserve this!"
"Deserve what, Mother? What am I doing that's so wrong?" Mary's mind rippled in a confused stream.
"What!" Mrs. Cuberle screamed, "What! Do you think I want people to point to you and say I'm the mother of an idiot? That's what they'll say, you'll see. Or," she looked up hopefully, "have you changed your mind?"
"No." The vague reasons, longing to be put into words.
"It doesn't hurt. They just take off a little skin and put some on and give you pills and electronic treatments and things like that. It doesn't take more than a week."
"No." The reason.
"Don't you want to be beautiful, like other people—like me? Look at your friend Shala, she's getting her Transformation next month. And she's almost pretty now."
"Mother, I don't care—"
"If it's the bones you're worried about, well, that doesn't hurt. They give you a shot and when you wake up, everything's moulded right. Everything, to suit the personality."
"I don't care, I don't care."
"But why?"
"I like me the way I am." Almost—almost exactly. But not quite. Part of it, however. Part of what Daddy and Grandpa meant.
"But you're so ugly, dear! Like Dr. Hortel said. And Mr. Willmes, at the factory. He told some people he thought you were the ugliest girl he'd ever seen. Says he'll be thankful when you have your Transformation. And what if he hears of all this, what'll happen then?"
"Daddy said I was beautiful."
"Well really, dear. You do have eyes."
"Daddy said that real beauty is only skin deep. He said a lot of things like that and when I read the books I felt the same way. I guess I don't want to look like everybody else, that's all." No, that's not it. Not at all it.
"That man had too much to do with you. You'll notice that he had his Transformation, though!"
"But he was sorry. He told me that if he had it to do over again, he'd never do it. He said for me to be stronger than he was."
"Well, I won't have it. You're not going to get away with this, young lady. After all, I am your mother."
A bulb flickered in the bathroom and Mrs. Cuberle walked uncertainly to the cabinet. She took out a little cardboard box.
"Time for lunch."
Mary nodded. That was another thing the books talked about, which the tapes did not. Lunch seemed to be something special long ago, or at least different. The books talked of strange ways of putting a load of things into the mouth and chewing these things. Enjoying them. Strange and somehow wonderful.
"And you'd better get ready for work."
"Yes, Mother."
THE office was quiet and without shadows. The walls gave off a steady luminescence, distributed the light evenly upon all the desks and[12] tables. And it was neither hot nor cold.
Mary held the ruler firmly and allowed the pen to travel down the metal edge effortlessly. The new black lines were small and accurate. She tipped her head, compared the notes beside her to the plan she was working on. She noticed the beautiful people looking at her more furtively than before, and she wondered about this as she made her lines.
A tall man rose from his desk in the rear of the office and walked down the aisle to Mary's table. He surveyed her work, allowing his eyes to travel cautiously from her face to the draft.
Mary looked around.
"Nice job," said the man.
"Thank you, Mr. Willmes."
"Dralich shouldn't have anything to complain about. That crane should hold the whole damn city."
"It's very good alloy, sir."
"Yeah. Say, kid, you got a minute?"
"Yes sir."
"Let's go into Mullinson's office."
The big handsome man led the way into a small cubby-hole of a room. He motioned to a chair and sat on the edge of one desk.
"Kid, I never was one to beat around the bush. Somebody called in little while ago, gave me some crazy story about you not wanting the Transformation."
Mary said "Oh." Daddy had said it would have to happen, some day. This must be what he meant.
"I would've told them they were way off the beam, but I wanted to talk to you first, get it straight."
"Well, sir, it's true. I don't. I want to stay this way."
The man looked at Mary and then coughed, embarrassedly.
"What the hell—excuse me, kid, but—I don't exactly get it. You, uh, you saw the psychiatrist?"
"Yes sir. I'm not insane. Dr. Hortel can tell you."
"I didn't mean anything like that. Well—" the man laughed nervously. "I don't know what to say. You're still a cub, but you do swell work. Lot of good results, lots of comments from the stations. But, Mr. Poole won't like it."
"I know. I know what you mean, Mr. Willmes. But nothing can change my mind. I want to stay this way and that's all there is to it."
"But—you'll get old before you're half through life."
Yes, she would. Old, like the Elders, wrinkled and brittle, unable to move right. Old. "It's hard to make you understand. But I don't see why it should make any difference."
"Don't go getting me wrong, now. It's not me, but, you know, I don't own Interplan. I just work here. Mr. Poole likes things running smooth and it's my job to carry it out. And soon as everybody finds out, things wouldn't run smooth. There'll be a big stink. The dames will start asking questions and talk."
"Will you accept my resignation, then, Mr. Willmes?"
"Sure you won't change your mind?"
"No sir. I decided that a long time ago. And I'm sorry now that I told Mother or anyone else. No sir, I won't change my mind."
"Well, I'm sorry, Mary. You been doing awful swell work. Couple of[13] years you could be centralled on one of the asteroids, the way you been working. But if you should change your mind, there'll always be a job for you here."
"Thank you, sir."
"No hard feelings?"
"No hard feelings."
"Okay then. You've got till March. And between you and me, I hope by then you've decided the other way."
Mary walked back down the aisle, past the rows of desks. Past the men and women. The handsome, model men and the beautiful, perfect women, perfect, all perfect, all looking alike. Looking exactly alike.
She sat down again and took up her ruler and pen.
MARY stepped into the elevator and descended several hundred feet. At the Second Level she pressed a button and the elevator stopped. The doors opened with another button and the doors to her Unit with still another.
Mrs. Cuberle sat on the floor by the T-V, disconsolate and red-eyed. Her blond hair had come slightly askew and a few strands hung over her forehead. "You don't need to tell me. No one will hire you."
Mary sat beside her mother. "If you only hadn't told Mr. Willmes in the first place—"
"Well, I thought he could beat a little sense into you."
The sounds from the T-V grew louder. Mrs. Cuberle changed channels and finally turned it off.
"What did you do today, Mother?" Mary smiled.
"Do? What can I do, now? Nobody will even come over! I told you what would happen."
"Mother!"
"They say you should be in the Circuses."
Mary went into another room. Mrs. Cuberle followed. "How are we going to live? Where does the money come from now? Just because you're stubborn on this crazy idea. Crazy crazy crazy! Can I support both of us? They'll be firing me, next!"
"Why is this happening?"
"Because of you, that's why. Nobody else on this planet has ever refused the Transformation. But you turn it down. You want to be ugly!"
Mary put her arms about her mother's shoulders. "I wish I could explain, I've tried so hard to. It isn't that I want to bother anyone, or that Daddy wanted me to. I just don't want the Transformation."
Mrs. Cuberle reached into the pockets of her blouse and got a purple pill. She swallowed the pill. When the letter dropped from the chute, Mrs. Cuberle ran to snatch it up. She read it once, silently, then smiled.
"Oh, I was afraid they wouldn't answer. But we'll see about this now!"
She gave the letter to Mary.
Mrs. Zena Cuberle
Unit 451 D
Levels II & III
City
Dear Madam:In re your letter of Dec 3 36. We have carefully examined your complaint and consider that it requires stringent measures. Quite frankly, [14]the possibility of such a complaint has never occurred to this Dept. and we therefore cannot make positive directives at the moment.
However, due to the unusual qualities of the matter, we have arranged an audience at Centraldome, Eighth Level, Sixteenth Unit, Jan 3 37, 23 sharp. Dr. Elph Hortel has been instructed to attend. You will bring the subject in question.
Yrs,
DEPT FMary let the paper flutter to the floor. She walked quietly to the elevator and set it for Level III. When the elevator stopped, she ran from it, crying, into her room.
She thought and remembered and tried to sort out and put together. Daddy had said it, Grandpa had, the books did. Yes, the books did.
She read until her eyes burned and her eyes burned until she could read no more. Then Mary went to sleep, softly and without realizing it, for the first time.
But the sleep was not peaceful.
"LADIES and gentlemen," said the young-looking, well groomed man, "this problem does not resolve easily. Dr. Hortel here, testifies that Mary Cuberle is definitely not insane. Drs. Monagh, Prinn and Fedders all verify this judgment. Dr. Prinn asserts that the human organism is no longer so constructed as to create and sustain such an attitude through deliberate falsehood. Further, there is positively nothing in the structure of Mary Cuberle which might suggest difficulties in Transformation. There is evidence for all these statements. And yet we are faced with this refusal. What, may I ask, is to be done?"
Mary looked at a metal table.
"We have been in session far too long, holding up far too many other pressing contingencies. The trouble on Mercury, for example. We'll have to straighten that out, somehow."
Throughout the rows of beautiful people, the mumbling increased. Mrs. Cuberle sat nervously, tapping her shoe and running a comb through her hair.
"Mary Cuberle, you have been given innumerable chances to reconsider, you know."
Mary said, "I know. But I don't want to."
The beautiful people looked at Mary and laughed. Some shook their heads.
The man threw up his hands. "Little girl, can you realize what an issue you have caused? The unrest, the wasted time? Do you fully understand what you have done? Intergalactic questions hang fire while you sit there saying the same thing over and over. Doesn't the happiness of your Mother mean anything to you?"
A slender, supple woman in a back row cried, "We want action. Do something!"
The man in the high stool raised his hand. "None of that, now. We must conform, even though the question is out of the ordinary." He leafed through a number of papers on his desk, leaned down and whispered into the ear of a strong blond man. Then he turned to Mary[15] again. "Child, for the last time. Do you reconsider? Will you accept the Transformation?"
"No."
The man shrugged his shoulders. "Very well, then. I have here a petition, signed by two thousand individuals and representing all the Stations of Earth. They have been made aware of all the facts and have submitted the petition voluntarily. It's all so unusual and I'd hoped we wouldn't have to—but the petition urges drastic measures."
The mumbling rose.
"The petition urges that you shall, upon final refusal, be forced by law to accept the Transformation. And that an act of legislature shall make this universal and binding in the future."
Mary's eyes were open, wide. She stood and paused before speaking.
"Why?" she asked, loudly.
The man passed a hand through his hair.
Another voice from the crowd, "Seems to be a lot of questions unanswered here."
And another, "Sign the petition, Senator!"
All the voices, "Sign it, sign it!"
"But why?" Mary began to cry. The voices stilled for a moment.
"Because—Because—"
"If you'd only tell me that. Tell me!"
"Why, it simply isn't being done, that's all. The greatest gift of all, and what if others should get the same idea? What would happen to us then, little girl? We'd be right back to the ugly, thin, fat, unhealthy-looking race we were ages ago! There can't be any exceptions."
"Maybe they didn't consider themselves so ugly."
The mumbling began anew.
"That isn't the point," cried the man. "You must conform!"
And the voices cried "Yes" loudly until the man took up a pen and signed the papers on his desk.
Cheers, applause, shouts.
Mrs. Cuberle patted Mary on the top of her head.
"There, now!" she said, happily, "Everything will be all right now. You'll see, Mary."
THE Transformation Parlor Covered the entire Level, sprawling with its departments. It was always filled and there was nothing to sign and no money to pay and people were always waiting in line.
But today the people stood aside. And there were still more, looking in through doors, TV cameras placed throughout the tape machines in every corner. It was filled, but not bustling as usual.
Mary walked past the people, Mother and the men in back of her, following. She looked at the people. The people were beautiful, perfect, without a single flaw.
All the beautiful people. All the ugly people, staring out from bodies that were not theirs. Walking on legs that had been made for them, laughing with manufactured voices, gesturing with shaped and fashioned arms.
Mary walked slowly, despite the prodding. In her eyes, in her eyes, was a mounting confusion; a wide, wide wonderment.
The reason was becoming less vague; the fuzzed edges were falling[16] away now. Through all the horrible months and all the horrible moments, the edges fell away. Now it was almost clear.
She looked down at her own body, then at the walls which reflected it. Flesh of her flesh, bone of her bone, all hers, made by no one, built by herself or someone she did not know. Uneven kneecaps, making two grinning cherubs when they bent, and the old familiar rubbing together of fat inner thighs. Fat, unshapely, unsystematic Mary. But Mary.
Of course. Of course! This was what Daddy meant, what Grandpa and the books meant. What they would know if they would read the books or hear the words, the good, reasonable words, the words that signified more, much more, than any of this.
The understanding heaped up with each step.
"Where are these people?" Mary asked half to herself. "What has happened to them and don't they miss themselves, these manufactured things?"
She stopped, suddenly.
"Yes! That is the reason. They have all forgotten themselves!"
A curvacious woman stepped forward and took Mary's hand. The woman's skin was tinted dark. Chipped and sculptured bone into slender rhythmic lines, electrically created carriage, stance, made, turned out.
"All right, young lady. We will begin."
They guided Mary to a large, curved leather seat.
From the top of a long silver pole a machine lowered itself. Tiny bulbs glowed to life and cells began to click. The people stared. Slowly a picture formed upon the screen in the machine. Bulbs directed at Mary, then redirected into the machine. Wheels turning, buttons ticking.
The picture was completed.
"Would you like to see it?"
Mary closed her eyes, tight.
"It's really very nice." The woman turned to the crowd. "Oh yes, there's a great deal to be salvaged; you'd be surprised. A great deal. We'll keep the nose and I don't believe the elbows will have to be altered at all."
Mrs. Cuberle looked at Mary and smiled. "Now, it isn't so bad as you thought, is it?" she said.
The beautiful people looked. Cameras turned, tapes wound.
"You'll have to excuse us now. Only the machines allowed."
Only the machines.
The people filed out.
Mary saw the rooms in the mirror. Saw things in the rooms, the faces and bodies that had been left; the woman and the machines and the old young men standing about, adjusting, readying.
Then she looked at the picture in the screen.
And screamed.
A woman of medium height stared back at her. A woman with a curved body and thin legs; silver hair, pompadoured, cut short; full sensuous lips, small breasts, flat stomach, unblemished skin.
A strange, strange woman no one had ever seen before.
The nurse began to take Mary's clothes off.
"Geoff," the woman said, "come[17] look at this, will you. Not one so bad in years. Amazing that we can keep anything at all."
The handsome man put his hands in his pockets.
"Pretty bad, all right."
"Be still, child, stop making those noises. You know perfectly well nothing is going to hurt."
"But—what will you do with me?"
"That was all explained to you."
"No, no, with me, me!"
"Oh, you mean the castoffs. The usual. I don't know exactly. Somebody takes care of it."
"I want me!" Mary cried. "Not that!" She pointed at the screen.
HER chair was wheeled into a semi-dark room. She was naked now, and the men lifted her to a table. The surface was like glass, black, filmed. A big machine hung above.Straps. Clamps pulling, stretching limbs apart. The screen with the picture brought in. The men and the woman, more women now. Dr. Hortel in a corner, sitting with his legs crossed, shaking his head.
Mary began to cry above the hum of the mechanical things.
"Shhh. My gracious, such a racket! Just think about your job waiting for you, and all the friends you'll have and how nice everything will be. No more trouble now."
The big machine hurtling downward.
"Where will I find me?" Mary screamed, "when it's all over?"
A long needle slid into rough flesh and the beautiful people gathered around the table.
They turned on the big machine.
THE END
URL
https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/36258/pg36258-images.html
-

William Shatner side Roger Corman discussing the film
TRANSCRIPT
0:00
foreign I remember this film in pieces it's been
0:06
so many years since uh we've worked on it that uh I remember the telephone call
0:14
I think it must have been from you saying you'd like me to be in the film and I was flushed From Success on
0:21
Broadway and and some major motion picture and this was a small picture this was uh not a large budgeted picture
0:28
and the thinking is you don't do that sort of thing if the promise of the of
0:35
the big films are there and I read the script and I think I may have told you in the
0:42
intervening years but you didn't know it then that I would have paid you money I wish you told me right I held it
0:51
but it was such a marvelous script from a wonderful book by Charlie Boy Charles Beaumont that you had to do one had to
1:00
do this film I believed in the picture very much I had had a string of successes at that
1:06
time I did something like 17 or 18 consecutive successes like the director I'd never had a failure and every idea I
1:15
gave to any production company was accepted this was the first script I
1:21
paid Chuck Beaumont for the book and he wrote the script and it was turned down by every company that had accepted all
1:30
of my other pictures for goodness so my brother and I pooled our funds and together with you we made the picture
1:36
yes but when you say pool your funds uh now that we're starting to talk about this I I recall that you more than
1:43
pooled your funds you you uh took loans on your houses yes we did as a matter of
1:48
fact I got a second mortgage on my house and and uh so there was a great deal
1:55
personally at stake for you uh not only financially but emotionally
2:00
emotionally the picture turned out very well it went to a number of film festivals including the Venice Festival
2:07
I won a couple of Awards as best director you won more Awards as best
2:12
actor the reviews were incredible I still remember one review in the New York Times
2:19
it started off by saying this motion picture is a major credit to the entire
2:24
American film industry it was the first film I ever made that lost money and
2:31
however luckily it didn't lose much it just lost a little bit so at least we didn't lose our houses yeah right that
2:38
second mortgage has been paid off indeed by the 16 or 17 successes that you had
2:45
um of course I guess success is defined by if it makes it makes it profit yes an
2:51
economic success an economic success uh but this film uh had a meaning and and a
2:59
sense to it that so many of of the films that I have made in the past hence uh before that and and and
3:07
after that did not have and I presume the same applies to you yes I believed
3:12
very deeply in the subject which was about racial integration in the South I
3:18
know you did and I think everybody connected with the film and that's one of the reasons why it's gone on to stay
3:26
alive so many years people remember it as an honest document for its time you
3:32
might say I'm in Social world I've come to do what I can for the time the integration problem Oh that but
3:40
that's all over I mean they've got 10 enrolled already in the schools and they're starting Monday yes I know
3:48
do you think it's right no well sure don't neither does nobody but it's the
3:54
law who's law to me as a Canadian coming down to the
4:00
United States uh I I was not aware of uh what was what the
4:07
turmoil was in in in in in in in in terms of the conflict black and white it
4:15
had no direct meaning to me because in Canada that that didn't exist
4:22
so I was I'm I read the newspapers and I would see the people and I would see
4:28
what was happening but I didn't insightfully intrinsically understand
4:34
what was going on to get into and live in behind somebody
4:40
who was being afflicted I did not get
4:45
into their heads until this picture until the intruder and it was only in
4:51
the Intruder did I did I was I forced to take a look at separate but equal
4:58
and integration and feeling of of uh of a partners because you're treated
5:07
differently you're an American citizen but you're not and I began to see what was taking place
5:14
and the ferment that was also taking place in a desire to change all that
5:22
uh this picture was an epiphany for me uh and working on it
5:30
it changed my life coming from California I was aware of
5:35
the difference between the races the uh problems of segregation but it was never
5:41
as strong obviously in the north this is in the South but it was there there was still uh a slight feeling of segregation
5:50
either even in a western or Northern State I had traveled a little bit in the
5:55
South and was amazed that in my own country this could be going on we read
6:03
about it we experienced a little bit of it in California but I remember the first time I was I think taking a bus
6:10
somewhere in New Orleans and I realized that all the blacks really were at the
6:17
back of the bus if you went to a theater the blacks were I think in the balcony
6:24
and the whites could be downstairs in the preferential seats and I realized
6:30
that this was institutionalized this was so built into their way of life that at
6:37
least for a period of time the whites accepted it as their natural right and
6:42
many blacks felt nothing could be done and I think it was although the great Revolution was to come later in the 60s
6:49
it was already starting I think coming out of World War II when blacks and whites had fought equally or
6:56
semi-equally in World War II and had come back to a society for which uh
7:03
blacks and Asian Americans as a matter of fact had fought and died for and had come back to find a society not equal
7:10
and they determined to do something about it right and and uh and when
7:15
you're not faced with it if you're in your own little white community and you
7:20
don't see the the trouble you tend to ignore it because it's
7:28
easier not to face it it's when you're looking at it through the eyes
7:33
of uh somebody who's been segregated do you understand the forces at work or
7:41
begin to understand and it's interesting to me that many people take the advances
7:46
of the last 30 40 years for granted my sons are both basketball players and
7:51
they play on fully integrated basketball teams and all that we've not yet reached Perfection we've made great strides I
8:00
tell them a little bit about what it was like and it's very hard for them to understand just in this short period of
8:06
History we've come so far well sir you see I represent the Patrick
8:12
Henry Society and what we'd like to know is just this how you stand with your four integration or against it that's a stupid question
8:18
young man I'm a southerner Sudan sedan thank you yeah I was born and raised in these parts so were my
8:25
folks that is you're against it of course I'm against it what's the matter
8:30
with you I don't remember exactly how I found the book The Intruder but as I recall a friend of mine had read it and
8:39
it simply recommended it to me as a good book because he knew that I was very
8:44
much interested in contemporary novels and I read the book and contacted Chuck
8:49
Bowman and luckily he lived in Los Angeles if he lived in Albuquerque he might never have made the film and I
8:56
talked to him and uh we worked out an arrangement and he wrote the script and again from inception it was something
9:03
that he believed in and I believed in I remember the first time I saw you we had not met you had done Marlo's play
9:11
Timberland which I thought was brilliant and I always remembered that performance
9:16
and uh so when I came to cast the picture I've been told you to come out to Hollywood and I remember it was the
9:23
simple thing at that point I gave the script to your age and who gave it to you we met and there it was yeah that's
9:29
interesting how one thing leads to another I think another element that makes the picture live
9:36
uh in the way it does it continues to live the way it does is the
9:42
emotions that are invested in the film not only prior to as we're talking now
9:49
I'm writing the script and getting the locations but in the actual filming we it was not
9:56
uh without its danger yes and that I think whether the audience
10:03
realizes it or not is reflected in some of the performances I mean there's genuine fear and Terror on some
10:12
locations where we were in Jeopardy particularly the Ku Klux Klan
10:17
drive-through scene which was the last scene we shot in the picture and at the
10:23
end of it because as you remember we were getting phone calls and threatening letters we shot that scene after having
10:29
checked out of our motel and at the conclusion of it we just stayed in the
10:34
cars and kept driving to St Louis I remember that and did you know do you remember that there was an actual
10:40
stabbing in the uh among the people lining the street somebody had been knifed yes I do remember that yeah so
10:48
the the danger was not uh was not in our own minds there were
10:54
if I remember uh there was a white gang it was a Black Gang both of whom were
11:00
dangerous but the most dangerous gang of all was a gang of ex-criminals who were
11:06
black and white yes so uh the vicious criminal element did not uh have its
11:13
roots in black or white they were just guys who wanted to get some money and uh and to hurt
11:21
somebody I could almost make up some sort of a moral there crime nose no racial
11:27
boundaries but that's true and in this case it's it's it's evident
11:33
um there was a guy that um I met huge man
11:40
tough and he was a source of irritant to the crew I
11:46
remember he was on the sidelines the whole time and
11:52
and he was Railing at us and jeering us and he was a real anime and he was
11:59
considered Dangerous by the by the police and by the by the crew
12:05
and I re forget now exactly how I met him whether he was brought in as a crew
12:13
member because he could take two stands I remember do you have a record of who
12:18
I'm talking about you know it does come back to me I think we did have him working because he was so strong because he was so strong and so potentially
12:24
dangerous so I talked to him and I found out that he had a great
12:32
quarter horse and I was interested in horses that he had his lucky chaps with which
12:37
he'd want I I forgotten probably cutting competitions
12:42
and he had the fastest car in the tri-state area of
12:48
and he had gone to Daytona with this uh Pontiac this jazzed up Pontiac and it
12:55
won some stuff and as I befriended him in the true manner of Southern generosity
13:02
he said anytime you want to ride my horse anytime you want to drive my car
13:09
I want you to do it well we were somewhere and Cairo Illinois was a
13:15
little further away and there was somebody there I forgotten now who I wanted to see and what it was I wanted
13:20
to see but I one day I asked him can I borrow your car and he said sure he said I want to show
13:27
you a couple of things he went to the trunk and inside that he opened the trunk and inside the trunk were his lucky chaps he says these are my lucky
13:34
chaps uh they brought me great luck in competition I they're right here don't
13:40
don't don't do you know just be sure that you don't open the trunk because these are very important to me
13:46
then he went to the truck the hood and Jack put the hood up and he said now
13:53
I want you to be careful you can see there are no air cleaners here that's because the raw air is sucked in
14:00
through the carburetor and and I've got four carbs here and it's the fastest car
14:07
in the tri-state area I won this is my great car this is a car it's one of a kind I love this car I love this car
14:13
very much so now I want you to be careful because the open mouth carburetor allows gasoline to be thrown
14:20
backwards as well so every so often it catches fire now come over here and behind the seat yeah that extinguisher
14:29
and he said here if ever you smell smoke
14:34
trip the hood get that off and just all you have to do is extinguish the fire
14:39
and it's fine I do that all the time so I said okay great the the fire extinguisher there had the hood
14:46
there and I had the trunk there and I drive to Cairo Illinois and I'm parked doing something on the curb I've
14:51
forgotten and somebody drives up alongside you say Hey sir your car is on fire
14:58
so I rushed to the trunk and I see Flames coming out of the trunk and now I
15:05
forget about the fire extinguisher I need something to put this fire on no I tripped the hood I tripped the trunk and
15:11
I run to the trunk and I grabbed some rags in the truck and I started beating out the fire and I'm beating out the fire and I'm beating out on it finally I
15:17
get the fire out and the engine is melted and I realized that the rags in my hands
15:24
are his lucky chips and this is one of the most dangerous
15:29
men we've ever met I had a tough time telling him what did he do what did he
15:35
do when you you told him I think he killed me yeah yes and we made a movie of that I remember a little different in
15:42
the later Seasons we had to resurrect me it was I I think
15:47
he was gracious about it actually I think he said oh I know something about it but it was it was
15:53
Dire and wonderful at the same time now he told me a very similar story but he said you know I'm getting a little tired
16:00
of this car and I've got it heavily insured and I've got this idiot that I'm gonna get to take the car
16:07
that's good but I remember some other tough uh
16:12
scenes do you remember the end of the picture where you uh and Leo Gordon and
16:18
Charlie Barnes the local uh black kid we had playing uh in the in the excuse me
16:25
which reminds me of the fact we only had four or five professional actors I think
16:30
it was you Leo Gordon uh Gene burnson and one other and all the
16:38
rest of them were local people and uh anyway in the final scene where which
16:44
takes place outside the school and Charlie is being swung back and forth in
16:50
the swing that was one of the roughest things we ever had we shot it in two days and the first day everything was
16:57
fine we got all our long shots all our establishing shots and when we went back for the second and concluding day and
17:04
this was the climax of the picture the sheriff of East Prairie Missouri
17:11
stopped us at the borders of the town and said you can't come into the town we had nothing else to do and I
17:18
remembered no place to shoot and I remembered that there were some swings in the public park in Sikeston so we
17:25
drove back to the public park and we shot during the morning shooting in
17:30
tight so you wouldn't see the uh the school on the public park swings and the
17:37
police of Sikeston came by to throw us out and you and I were working on the
17:43
set and my brother was doing a greater not a greater an equal job of acting talking to the police because he knew I
17:50
needed a little time to finish the scene and saying well I don't understand officers can you explain exactly what
17:55
your attitude is just double talking we kept shooting until it was time to break for lunch and I gave the sign to my
18:02
brother and my brother said okay we'll understand we understand we'll leave we'll leave town Gene your brother Gene
18:10
has not changed at all he double talks no matter what indeed and we still had
18:17
half a day of shooting to do and during lunch while everybody was breaking for lunch I had remembered another school
18:22
that we had scouted and rejected because it was out in the country and I drove to that school and uh
18:29
it was summer vacation and there was nobody there so we went to the school without any permits or anything we
18:36
didn't pull from that sort of thing and we shot the concluding part of the scene on the swings there and nobody has ever
18:44
noticed the fact that the final scene was shot in three different locations and the swings were of different heights
18:51
and it seen plays and I think it's partially the way we shot it and partially your performance was so strong
18:58
they were looking at you this town I'm talking about texting yeah
19:04
[Applause] people
19:09
something happened today 10 Negroes went into the caxton high school and sat
19:16
with the white children there nobody stopped them nobody turn them off
19:24
and you know what they're saying that means they're safe
19:29
as you all don't give a darn whether the whites mixed with the blacks because he didn't fight against it the
19:35
um the denuma of that film was uh also uh
19:40
Vivid still vividly lives in my mind um you had chosen as a location a a
19:47
courthouse an exterior of a courthouse uh and steps that went up and and now
19:53
the character I was playing was about to Harang the mob to rise up and and
20:00
pillage um so that the integration would not take place and
20:06
for several days before that final scene uh which was I believe at the end of the
20:13
week we had done a lot of yelling and jumping and screaming and running both from the
20:19
police from the gangs and uh and also on camera my voice was was shot and I had
20:27
the day before off so if it was a Friday night that we were going to shoot I had Thursday night off and I'd gone to the
20:34
doctor in the local Town who said you've got laryngitis which is fatigue and
20:40
overuse of the muscle The Voice you need to rest and you may be able to speak I could I
20:45
could not speak like that and I had this long several pages of speech to make
20:52
so I said can you give me some sleeping pills I don't work tomorrow night can you give me some sleeping pills and put
20:59
me to sleep for 24 hours which is what I did I took sleeping
21:05
pills and actually I remember waking up and thinking it was 12 hours later but
21:10
it was only a couple of hours later so I popped a couple more and finally I drugged myself out to be out of it for
21:18
24 hours during which if I had to speak like get something to eat I wrote it out
21:24
I never used my voice and I didn't use my voice when we went to location I did
21:29
not speak I wrote out the notes and you set up
21:35
over my shoulder onto the crowd first and then when you finished all your coverage facing away from me or over my
21:43
back onto the crowd and I didn't speak to the crowd even on their reactions you had it read by somebody either yourself
21:49
or people already read but what we wrote was not totally innocuous that's exactly
21:55
right you wrote innocuous things that's right it was you know buy at the sacks
22:00
you know Macy's window or whatever drink uh Perry
22:06
no I think I've got enough uh product placement in there yes um and work with Priceline
22:12
and buyers tickets uh and all of which was meaningless to the audience and then
22:18
you reverse and you went way away from me I still didn't speak and finally you were on me for the medium and close
22:23
shots by that time it was after midnight and the crowd realized the truth that
22:30
everybody who's not connected with the movie ultimately realizes that is making a movie like watching a horse show is
22:37
boring unless you're intimately connected with the details of of what it is you're doing so they had long since
22:43
left there were 10 people left in the out of the hundreds that had turned up and I began my speech and spoke the
22:50
speech for the first time with great gratitude that my voice was working but nobody was there and the following day I
22:58
think it was you and I were walking along the Main Street and the guy from the newspaper
23:04
called us over and he said do you realize that where you were last night that tree that was uh in the courtyard
23:12
was a tree that was used for lynching that people in the audience that you had last night would have remembered
23:20
uh uh the the terrible tragic events that that uh that
23:27
took place there and that had I spoken these fiery words that Charles Beaumont
23:35
had written they might we might have had a different ending on our hands very fast ended well
23:44
as a matter of fact I do remember that and I remember also the fact that people
23:49
did not totally know exactly the details of what you were doing the script we
23:54
gave handed out was a little bit different than the script we actually shot and I remember you had a group of
24:01
followers that I had chosen or there were sort of the guys who sat around the town square whittling and spitting and
24:06
talking they had great faces and they were loyal followers and well you were
24:13
saying these various inflammatory uh anti-integration as sentiments they were
24:19
yelling and applauding they were with you all the way and they thought you were a good guy and they were really
24:26
disappointed when they found out at the end of the picture that you were a bad guy they agreed with you all the way and
24:31
that the school's integrated yes you mean that's the way it is
24:36
and I'm willing to give my life if that'd be necessary to see that my country stays free
24:44
White and American [Applause]
25:03
everybody
25:11
so making the film uh was a a risk to
25:17
you as a personally financially and and I'm sure artistically uh and to you and
25:26
the rest of us it was a risk uh physically uh to make the film there was a lot at stake there was a lot of stake
25:33
and uh although it was not at that time of Commercial Success eventually because it's hung on so long it has finally
25:40
broke the black but emotionally I still remember it uh as one of the best
25:46
pictures of one of the films I remember most fondly and I'm most proud of and I
25:52
think your performance was brilliant the number of awards you won with that performance was amazing it was it was a
25:58
wonderful opportunity the Intruder was named several things as it went through its it was it started as
26:05
the Intruder and it was not a commercial success so uh a sort of an exploitation
26:12
distributed from the south that I knew said he could make this picture uh
26:18
commercially successful and I said fine and he put some wild title on it and it
26:24
did a little bit better but I don't even remember what the title was I have blocked it out of my mind the garbage man yes whatever and it's gone back to
26:31
being the Intruder and it's had a very strange life and keeps going for
26:37
instance the British Film Institute asked me if they could release it I was not aware that they did this in England
26:44
as part of some sort of a series of socially committed films this was two
26:50
years ago and it was a big success in England and of the films in that series
26:55
that they put in a series of art theaters it was the highest grossing uh and it got wonderful reviews so the and
27:04
I think what it is and I've always believed this if the people making the film the writer
27:12
director producer actors even the crew and so forth really believe in a film
27:18
and make it honestly and truthfully the film itself is permeated with that I
27:24
agree but I think it uh as they say a fish in this case uh the the vehicle uh
27:32
the the the the the the Cinematic vehicle is being led by the
27:38
head the the fish tanks at the head I think the the uh the uh the film is led
27:45
by the director and the passions and the and the uh
27:50
first force of creativity is the directors and it was you Roger that took
27:57
us uh there and was you your courage and your your commitment to your picture and
28:04
um and one doesn't that doesn't come to mind
28:09
uh when you think of a Roger Corman film you think of a Roger Corman film you
28:14
think of the wonderful talents that were started that you you spotted early on that you made for a price you taught a
28:21
lot of people in this industry to make films clean and uh and with no fat on
28:28
them at all uh and and put every penny that you spend put it up on the screen and not in a craft service table
28:36
uh it's a lesson I learned uh and am applying even as we speak You're
28:42
directing a film now I'm directing a film now and I'm searching for it's not
28:48
a controversial film but it's difficult to make a film
28:54
cheaply anymore uh people have gotten sophisticated
28:59
about asking for money for locations and and for performing performing is I'm it's all it's quite different and yet
29:07
it's not because the need if you have a limited amount of money and you want to make a film The need to put the money on
29:14
the screen is the same yes and you laid down some fine ground work there that
29:22
we're all still trying to follow but I've always believed is what ultimately
29:27
counts is what is on the screen not how many people as you say the craft service table although you can have pretty good
29:33
food on the craft service table not what's behind the camera ultimately what
29:38
is there and uh I think on the Intruder the fact that we shot it on the actual
29:44
locations with primarily non-actors who possibly their lack of ability showed
29:50
but the realism of what they did showed and talking about costs and so forth
29:55
that I remember we shot it in three weeks on a budget of around 70 or 80 000
30:00
which was would be impossible today but was pretty tough then and I think back
30:07
of it uh back on it as uh a kind of a milestone for me and uh a brilliant
30:15
performance for you are we both gone on we've had good careers you've had a great career and I think we can look
30:21
back at this film with pride and I do
English (auto-generated)
-
-
 1
1
-
- Report
-
-
KWL Live Q&A – Accessibility Tips for Authors with Wendy Reid started at noon
MY THOUGHTS AS I LISTENED
12:02 what does accessibility mean?
The main focus on the needs and requirements for people with disabilities12:03 How did you get involved?
She did work for the world wide web technical standards. She mostly work on epub and digital publishing. She got a lot of insight from people in disability community cause they,epub and similar, are so important for people with disabilities.12:05 The exercise to using the audio on her phone to navigating to her phone by audio was a challenge.
Most tools are not accessible but the disability community members have figured out workarounds
if you want to know more about accessiblity in kobo email the following
< kobo-accessibility@rakuten.com >12:08 What is your day to day at Kobo
A lot of meetings. A lot of time researching trying to find the best way to do things. Accessibility on a tech company with a lot of different interfaces is busy.
Another interview side wendy
< https://www.kobo.com/blog/learn-how-kobo-makes-reading-more-accessible >12:12 What will you say to an author who ask with accessibility?
We all deal with accessibility or disability issues in life. You are planning for your future self and being inclusive of your audience.
Captions are designed for people who are hard to hear but they are a huge accessibility option12:15 do you know about accessibility options that authors need to be aware of, top complaints?
Image descriptions. If you are using a screen reader, and an image isn't described it is frustrating to the reader. Around NAvigation, have a really good table of contents. Name your chapters, or subsections. Table your headings. That structure will help those who have a hard time seeing.12:18 How will an author know if their file is as accessible as can be?
if you are not creating the epub yourself, you can mark themself up in word. they all have accessibility checkers in them. Make sure headings are headings. Describe all images.
Question to ask platform you distributing to, are you using that information to make epub. Are you making sure the heading 1 in word is heading 1 in epub.
Alot of companies put disabled users to the side but one in five worldwide have a disability.12:22 how detailed should alt text should be
There is no one way to make alt text. <She gives a great example of describing a cat> How to present a science fiction map, may be really long. The author has to decide which is best.12:25 Epub files
It is better to make a bigger book be split into multiple files.<one thing you guys can do is allow people to have the choice of retaining old interfaces. Some people feel better accessibility with older interfaces>
12:28 Accessibility Checker
Kobo will add it.12:31 How do you handle alt text in covers?
We don't have that information cause and can't do it at scale but inside your book, describe your cover.12:32 Can they work on fonts on covers?
Make covers readable. She has seen covers that is barely visible in small image form. Be mindful of how busy an image is. Make text stand out more. She gets complaints, try testing covers in greyscale and it is hard to see. Her father's love sending screen shots in ereader.Book on history of audiobook
< https://www.kobo.com/us/en/ebook/the-untold-story-of-the-talking-book-3 >
< https://www.kobo.com/us/en/audiobook/the-untold-story-of-the-talking-book-2 >12:35 what about accessibility in audio books?
Underexplored area. Audiobooks were developed to be accessibile. Soldiers from world war 1 who lost their vision to be able to read. Two essential things: If you have images in book, describe in audio. Audiobook structure, she likes to know chapters in table of contents, not tracks.
She uses a book that came out two months ago and it had track 1 track 2 not chapters.Audiobook format in Kobo
< https://kobowritinglife.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360059385511-How-to-Upload-Your-Audiobook-Directly-on-Kobo >12:40 What can authors do now in terms of metadata?
Can include in description. The summary is the best place to do that. DRM is not really accessible. Kobo is looking at implementing more accessibility formats in DRM. But DRM isn't great for accessibility.12:42 Is anything authors should be aware of for external links?
Put in link text. Recommend don't using link text that uses vague things. Use the alt text.12:44 How to make websites more accessible?
Describe all images. Describe all links. Wix or squarespace have accessibility options. You can do yourself. Ask about color palette. No highlighter color on black. Try to avoid putting text on top of book covers. Highly recommend using simple fonts, dyslexia or visually processing issues, and the most readable fonts are times new roman, helvitica, georgia, callibri. Describe book covers.12:48 any newsletter or email practices?
Same issues for the websites or books. Alot of design fundamentals cross into accessibility fundamentals.12:52 what about accessibility in social media?
Alt text are needed for every image. Highly recommend. If a platform doesn't have it, use the caption. Alot of tiktokers use captions in videos. Apply captions for video post. Higly recommend reviewing captions for automated captions. Use the most simple captions , it is best for accessibility. They need to detect whether you have your own captions cause you get double captions at times. Youtube provide audio descriptions, consider that.12:57 about emoji's?
Use emoji's carefully. Every emoji has a name. use simplest, and don't open with emoji's.1:00 What do you think the publishing industry need to be more accessible ?
The publshing industry in some countries, canada included, the biggest problem is funding, and going through backlist and making them more accessible. Alt text is hard for very old books. Publishers try to figure that out. How do we make text that are visually complex , more accessible.List of her links in comments
https://kobowritinglife.com/2023/08/03/kwl-live-qa-accessibility-tips-for-authors-with-wendy-reid/Ace by DAISY – accessibility checker for EPUB < https://daisy.org/activities/software/ace/ >
DAISY Knowledge Base, everything you need to know about coding accessible EPUBs < http://kb.daisy.org/publishing/docs/epub/ >
Accessible Publishing Learning Network – lots of excellent resources! < https://apln.ca/ >
WAVE Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool < https://wave.webaim.org/ >
Colour Contrast, an easy to use colour contrast checker < https://colourcontrast.cc/ >
Accessible Social, a resource for creating accessible social media content < https://www.accessible-social.com/ >
Social Visual Alt Text, fun web extension for viewing alternative text on social media < https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/social-visual-alt-text/bkpbmomfemcjdeekdffmbohifpndodm >
WordToEPUB < https://daisy.org/activities/software/wordtoepub/ >
MY CLOSING THOUGHTSI thought about accessibility. If accessibility was considered from the beginning of most processes it would undo alot of the schemes/scams/ aspects of entertainment/social media/wesbites or other.
For example, I like the mandolorian show from Disney. If someone is blind and they can't see the Mandolorian maybe they have an audio read version available. So they can hear each episode absent commercials. But imagine if you are listening to an on demand film, like Godzilla, like from TNT of the warner bros group in Discovery. Imagine you hear:"this thing killed my wife!, have you ever had bad bowels, Well try..." The commercial break is by default a terrible element. For someone who can only hear they are bound to hear a commercial where those with sight can mute and move on and come back.
Accessibility if engineered optimally will delete many methods of commercialization in entertainment or media through electronic means.
-
The following is my neutral reply to a reply to my words appended after.
science just means knowledge.
Using my own linguistic style, I will say, Researchers , who are able to be concurred to or refuted by others, suggest based on their studies that bias, communal positions based on interpreting race, has no genetic source.
I concur that biases , like linking intelligence or emotional quality to a racial factor like phenotype or gender, are not genetically based most of the time.
Yes, one can argue that downs syndrome, which is a known, publicly known, genetically derived condition with symptoms of mental inaptitude or uncommon difficulty does at the least prove genetics has instances where it influences intelligence, but the genomes which tend to be variant in those with downs syndrome do not occur bounded to the presence of other genetic markers for gender or phenotype or other, at least to my knowledge.
Yes, one can argue that women during pregnancy, which is a genetically based condition < men if healthy can not get pregnant whereas a woman who is healthy can> , have a long history of recorded emotional swings but like downs syndrome, it isn't bounded to the presence of other genomes.
I will speak for myself.
I am not being dishonest, I have said no lie, or betrayed my thinking. Nor have I spoken illogically, absent a structured reason, or ignorantly, meaning absent knowledge.
And as this is the African American Literature Book Club, I think a greater point is being missed. The most important point of the trilog and that is use of words, especially in the black community of the usa.
In literature, the use of words is logically the most important aspect of literature, not culturally or heritagewise but logically. That is why the word gay doesn't mean happy anymore for most people in the anglophone.
To me, as I said before, I didn't explain myself to get anyone else to change. I explained myself cause I felt it was warranted as functional reasoning that needs to be emitted, and not silent. I don't think any conflict exist between the three in the trilog. All explained themselves, and I said what Troy said makes sense, is logical, based on the elemental parts. But my elemental parts are other. It doesn't make me right or the other two wrong., or them right and me wrong. We have two different definitions of race that have no middle point and in my eyes, none of us have a reason to utilize the other, unless we as individuals want to.
But, Troy, a member of this group, asserted at the end, that I , or anyone else, shouldn't have a different use of words than websters or majority users. And I oppose that 100%. Just because websters has decided on a definition doesn't make it irrefutable , regardless of how many people are taught it or are indoctrinated to it.
And this goes into the black community. If one hundred black people live in a room and 99 say things one way and have a different mind to the room, why should the one be uncomfortable because they are alone. Some speak of individualism quite often in the black community in the usa, yet they often suggest in parallel that individualism should give into communalism when one is not comfortable, defined as opposed to a majority.
And yes, I reject more than one word in websters. As a poet I study words and I have found heavy levels of misuse in words. So much so I do it often myself, cause the USA environment has made common a lot of incorrect word usages. I will love to have a chance to work on a dictionary for a less known or used language. I wish Black people in the USA had not thrown away our many dialects for .... websters.
I nearly hate the blanc french but I have always been a fan of the following.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Académie_Française
Why? I think the french are correct in the maintenance of language. In the same way the architects of timbuktu are correct in making buildings where aspects to their maintenance or repair is part of their final structure. Every language should have some organization to manage it to be within itself. American English is a terrible language in that way. It is unorganized, muddled, and ugly in the allowance of atemporal disjunction.
The USA thought about it
http://www.languagepolicy.net/archives/Adams.htm
The continental congress logic wasn't flawed. From the beginning they realized, that having language be fluid opened up allowances in expression, which allows for the composite nation speech point.
Composite nation from frederick douglass
But Adams was correct. Language dictates the populace. When you look at the usa today and the individual liberty of it, it can be argued that the freedom of language plus the lack of management of language is a key to its populace's makeup. American English is looking to be mixed , so to speak.
But it is interesting that so many Black people in my creative circle, writers especially, are willing to suggest my use of words is false based not on anything official, but merely majority use, absent any management. I suggest a managed and researched language is best in any community, or you end up talking muddle.
John Adams penned this proposal while on a diplomatic mission to Europe during the Revolutionary War. Formally entitled "A Letter to the President of Congress," it was dispatched from Amsterdam on September 5, 1780.
As eloquence is cultivated with more care in free republics than in other governments, it has been found by constant experience that such republics have produced the greatest purity, copiousness, and perfection of language. It is not to be disputed that the form of government has an influence upon language, and language in its turn influences not only the form of government, but the temper, the sentiments, and manners of the people. The admirable models which have been transmitted through the world, and continued down to these days, so as to form an essential part of the education of mankind from generation to generation, by those two ancient towns, Athens and Rome, would be sufficient, without any other argument, to show the United States the importance to their liberty, prosperity, and glory, of an early attention to the subject of eloquence and language.
Most of the nations of Europe have thought it necessary to establish by public authority institutions for fixing and improving their proper languages. I need not mention the academies in France, Spain, and Italy, their learned labors, nor their great success. But it is very remarkable, that although many learned and ingenious men in England have from age to age projected similar institutions for correcting and improving the English tongue, yet the government have never found time to interpose in any manner; so that to this day there is no grammar nor dictionary extant of the English language which has the least public authority; and it is only very lately, that a tolerable dictionary has been published, even by a private person, and there is not yet a passable grammar enterprised by any individual.
The honor of forming the first public institution for refining, correcting, improving, and ascertaining the English language, I hope is reserved for congress; they have every motive than can possibly influence a public assembly to undertake it. It will have a happy effect upon the union of the States to have a public standard for all persons in every part of the continent to appeal to, both for the signification and pronunciation of the language. The constitutions of all the States in the Union are so democratical that eloquence will become the instrument for recommending men to their fellow-citizens, and the principal means of advancement through the various ranks and offices of society.
In the last century, Latin was the universal language of Europe. Correspondence among the learned, and indeed among merchants and men of business, and the conversation of strangers and travellers, was generally carried on in that dead language. In the present century, Latin has been generally laid aside, and French has been substituted in its place, but has not yet become universally established, and, according to present appearances, it is not probable that it will. English is destined to be the next and succeeding centuries more generally the language of the world than Latin was in the last or French is in the present age. The reason of this is obvious, because the increasing population in America, and their universal connection and correspondence with all nations will, aided by the influence of England in the world, whether great or small, force their language into general use, in spite of all the obstacles that may be thrown in their way, if any such there should be.
It is not necessary to enlarge further, to show the motives which the people of America have to turn their thoughts early to this subject; they will naturally occur to congress in a much greater detail than I have time to hint at. I would therefore submit to the consideration of congress the expediency and policy of erecting by their authority a society under the name of "the American Academy for refining, improving, and ascertaining the English Language." The authority of congress is necessary to give such a society reputation, influence, and authority through all the States and with other nations. The number of members of which it shall consist, the manner of appointing those members, whether each State shall have a certain number of members and the power of appointing them, or whether congress shall have a certain number of members and the power of appointing them, or whether congress shall appoint them, whether after the first appointment the society itself shall fill up vacancies, these and other questions will easily be determined by congress.
It will be necessary that the society should have a library consisting of a complete collection of all writings concerning languages of every sort, ancient and modern. They must have some officers and some other expenses which will make some small funds indispensably necessary. Upon a recommendations from congress, there is no doubt but the legislature of every State in the confederation would readily pass a law making such a society a body politic, enable it to sue and be sued, and to hold an estate, real or personal, of a limited value in that State.
ORIGINAL REPLY
-
The following is my neutral reply to a reply to my words appended after.
science just means knowledge.
Using my own linguistic style, I will say, Researchers , who are able to be concurred to or refuted by others, suggest based on their studies that bias, communal positions based on interpreting race, has no genetic source.
I concur that biases , like linking intelligence or emotional quality to a racial factor like phenotype or gender, are not genetically based most of the time.
Yes, one can argue that downs syndrome, which is a known, publicly known, genetically derived condition with symptoms of mental inaptitude or uncommon difficulty does at the least prove genetics has instances where it influences intelligence, but the genomes which tend to be variant in those with downs syndrome do not occur bounded to the presence of other genetic markers for gender or phenotype or other, at least to my knowledge.
Yes, one can argue that women during pregnancy, which is a genetically based condition < men if healthy can not get pregnant whereas a woman who is healthy can> , have a long history of recorded emotional swings but like downs syndrome, it isn't bounded to the presence of other genomes.
I will speak for myself.
I am not being dishonest, I have said no lie, or betrayed my thinking. Nor have I spoken illogically, absent a structured reason, or ignorantly, meaning absent knowledge.
And as this is the African American Literature Book Club, I think a greater point is being missed. The most important point of the trilog and that is use of words, especially in the black community of the usa.
In literature, the use of words is logically the most important aspect of literature, not culturally or heritagewise but logically. That is why the word gay doesn't mean happy anymore for most people in the anglophone.
To me, as I said before, I didn't explain myself to get anyone else to change. I explained myself cause I felt it was warranted as functional reasoning that needs to be emitted, and not silent. I don't think any conflict exist between the three in the trilog. All explained themselves, and I said what Troy said makes sense, is logical, based on the elemental parts. But my elemental parts are other. It doesn't make me right or the other two wrong., or them right and me wrong. We have two different definitions of race that have no middle point and in my eyes, none of us have a reason to utilize the other, unless we as individuals want to.
But, Troy, a member of this group, asserted at the end, that I , or anyone else, shouldn't have a different use of words than websters or majority users. And I oppose that 100%. Just because websters has decided on a definition doesn't make it irrefutable , regardless of how many people are taught it or are indoctrinated to it.
And this goes into the black community. If one hundred black people live in a room and 99 say things one way and have a different mind to the room, why should the one be uncomfortable because they are alone. Some speak of individualism quite often in the black community in the usa, yet they often suggest in parallel that individualism should give into communalism when one is not comfortable, defined as opposed to a majority.
And yes, I reject more than one word in websters. As a poet I study words and I have found heavy levels of misuse in words. So much so I do it often myself, cause the USA environment has made common a lot of incorrect word usages. I will love to have a chance to work on a dictionary for a less known or used language. I wish Black people in the USA had not thrown away our many dialects for .... websters.
I nearly hate the blanc french but I have always been a fan of the following.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Académie_Française
Why? I think the french are correct in the maintenance of language. In the same way the architects of timbuktu are correct in making buildings where aspects to their maintenance or repair is part of their final structure. Every language should have some organization to manage it to be within itself. American English is a terrible language in that way. It is unorganized, muddled, and ugly in the allowance of atemporal disjunction.
The USA thought about it
http://www.languagepolicy.net/archives/Adams.htm
The continental congress logic wasn't flawed. From the beginning they realized, that having language be fluid opened up allowances in expression, which allows for the composite nation speech point.
Composite nation from frederick douglass
But Adams was correct. Language dictates the populace. When you look at the usa today and the individual liberty of it, it can be argued that the freedom of language plus the lack of management of language is a key to its populace's makeup. American English is looking to be mixed , so to speak.
But it is interesting that so many Black people in my creative circle, writers especially, are willing to suggest my use of words is false based not on anything official, but merely majority use, absent any management. I suggest a managed and researched language is best in any community, or you end up talking muddle.
John Adams penned this proposal while on a diplomatic mission to Europe during the Revolutionary War. Formally entitled "A Letter to the President of Congress," it was dispatched from Amsterdam on September 5, 1780.
As eloquence is cultivated with more care in free republics than in other governments, it has been found by constant experience that such republics have produced the greatest purity, copiousness, and perfection of language. It is not to be disputed that the form of government has an influence upon language, and language in its turn influences not only the form of government, but the temper, the sentiments, and manners of the people. The admirable models which have been transmitted through the world, and continued down to these days, so as to form an essential part of the education of mankind from generation to generation, by those two ancient towns, Athens and Rome, would be sufficient, without any other argument, to show the United States the importance to their liberty, prosperity, and glory, of an early attention to the subject of eloquence and language.
Most of the nations of Europe have thought it necessary to establish by public authority institutions for fixing and improving their proper languages. I need not mention the academies in France, Spain, and Italy, their learned labors, nor their great success. But it is very remarkable, that although many learned and ingenious men in England have from age to age projected similar institutions for correcting and improving the English tongue, yet the government have never found time to interpose in any manner; so that to this day there is no grammar nor dictionary extant of the English language which has the least public authority; and it is only very lately, that a tolerable dictionary has been published, even by a private person, and there is not yet a passable grammar enterprised by any individual.
The honor of forming the first public institution for refining, correcting, improving, and ascertaining the English language, I hope is reserved for congress; they have every motive than can possibly influence a public assembly to undertake it. It will have a happy effect upon the union of the States to have a public standard for all persons in every part of the continent to appeal to, both for the signification and pronunciation of the language. The constitutions of all the States in the Union are so democratical that eloquence will become the instrument for recommending men to their fellow-citizens, and the principal means of advancement through the various ranks and offices of society.
In the last century, Latin was the universal language of Europe. Correspondence among the learned, and indeed among merchants and men of business, and the conversation of strangers and travellers, was generally carried on in that dead language. In the present century, Latin has been generally laid aside, and French has been substituted in its place, but has not yet become universally established, and, according to present appearances, it is not probable that it will. English is destined to be the next and succeeding centuries more generally the language of the world than Latin was in the last or French is in the present age. The reason of this is obvious, because the increasing population in America, and their universal connection and correspondence with all nations will, aided by the influence of England in the world, whether great or small, force their language into general use, in spite of all the obstacles that may be thrown in their way, if any such there should be.
It is not necessary to enlarge further, to show the motives which the people of America have to turn their thoughts early to this subject; they will naturally occur to congress in a much greater detail than I have time to hint at. I would therefore submit to the consideration of congress the expediency and policy of erecting by their authority a society under the name of "the American Academy for refining, improving, and ascertaining the English Language." The authority of congress is necessary to give such a society reputation, influence, and authority through all the States and with other nations. The number of members of which it shall consist, the manner of appointing those members, whether each State shall have a certain number of members and the power of appointing them, or whether congress shall have a certain number of members and the power of appointing them, or whether congress shall appoint them, whether after the first appointment the society itself shall fill up vacancies, these and other questions will easily be determined by congress.
It will be necessary that the society should have a library consisting of a complete collection of all writings concerning languages of every sort, ancient and modern. They must have some officers and some other expenses which will make some small funds indispensably necessary. Upon a recommendations from congress, there is no doubt but the legislature of every State in the confederation would readily pass a law making such a society a body politic, enable it to sue and be sued, and to hold an estate, real or personal, of a limited value in that State.
ORIGINAL REPLY
-
She makes a number of points that are not contiguous.
1) colleges admission process- Some of you may know history but the tragedy of the history of colleges is no college in the usa started as a public institution. I rephrase, most colleges start as race based organizations on whatever racial parameters the creators and financiers of the college set. So my first point is separating colleges started with racial entry rules, against colleges started as a truly public educational institution.
If I start and finance a college for black people, as I define them, exclusively and a white person, as I define them, wants to join, shouldn't my school be allowed to block this person no matter what?
Forcing a college to find someone to join their school who fits the scholastic racial requirements but not the financial or phenotypical racial requirements is what affirmative action is in the usa. The idea is to force only scholastic entry requirements but schools are financed.
If a christian finances a school for christians only shouldn't a muslim be banned from joining no matter what?
If a woman finances a school for women only, shouldn't a male be banned from joining no matter what?
2) coming from being raised in majority black towns/communities in the usa and being into majority white educational institutions explains how some want to use integration. A smart person from a black town should be able to go to a historical black college since many of them were started in the 1800s. But, what is the point? The point of the black going to the ivy league isn't about education, it is about communal integration. The idea is, in an environment where the phenotypical + financial race is not their own, the black fiscally poor student will intermingle side the rich white and potentially integrate into rich white society in some way or form. The problem is the pretense of educational betterment is deleted with this point. The idea that harvard is this elite place educationally isn't why the affirmative action is needed, cause harvard isn't. The truth that harvard is a communal zone for the financially wealthy or powerful who are usually white is why affirmative action is needed, cause through harvard maybe the halls of power or channels of business ownership may change through the communal connection.
Why have so many Black people put so much effort in non black schools but then complain about non black schools being communally resistant to them?
Do black people who go to Ivy LEague schools hate Historical Black Colleges?
3) The universality of affirmative action creates incongruent scenarios. In Mississippi an all white elementary school had affirmative action placed upon it so seats for black children were made. BUT, is any all white elementary school the equivalent to harvard? Harvard is a place for adults , truly of the greatest financial wealth. But is the all white elementary school the place of financial wealth or adults? The answer is no. Jefferson Davis elementary school in Mississippi isn't Harvard and too many all white educational institutions are more like jefferson davis elementary in mississippi, all white but not a hall of power or financial influence, and far from harvard or exeter.
4) Coming from being raised in majority black towns/communities in the usa and being into majority non black educational institutions puts black individuals in communities of disbelief. Of course among black people, a black child that has a talent or skill is merely praised. but around non blacks, it is questioned. All communities do this. White men can jump? It happens. Humans like to be in their own subgroups, their own kinds, ala Anita in west side story. The problem is why do people not raise their children to know this? I don't like when any person doesn't realize being the only other in a room will yield to being treated as unwanted, that makes perfect sense.
5) Black women in particular's rant about white inheritance. Yes, black women, white people are rarely like Mrs. PArkington. < https://aalbc.com/tc/profile/6477-richardmurray/?status=2371&type=status > who cut their descendants from the money if they don't earn or unwarrant it. but that is part of why you get money. And I argue in the black community many black people have developed an inverted sense of wealth through bloodline. Whites usually get money and believe it to be for their next generations no matter what, to make their life easier/lazier no matter what. But many black people seem to have this meritocracy idea in inheritance which is at best ideal for the usa that never was or will be, but at worst is a detriment to black growth. Yes, rich whites built harvard/yale/stanford/massachusetts instittue of technology/colombia , they built the museusm in new york city, shouldn't their children have a free ride in the institution that wouldn't exist if not for their forebears.
Again, if I started and financed a school, and after I am dead, shouldn't my descendants have free admittance in the school? I built the damn school, if one spot is open shouldn't my descendant have the seat over any other, black or white or with better grades?
6) and Yes, the whole point of the white community in the usa or the british colonies before it is, money talks. Yes, the descendants of the genocidal murderers to Native Americans + Enslavers to Blacks reap the rewards. That is fiscal capitalism. That is the usa. The USA isn't about equality, isn't about fairness, isn't about helping the weak or unopportune. It is about benefiting for self over others through their pain for your own benefit. And maintaining the benefits you earned for your descendants over the descendents of those you murdered or abused. Yes, that is the USA.
Why is it so many black people don't know this?
Why do so many black people in the usa sound ignorant/stupid/dumb/foolish to what I said in point 6)?
@africanheritagecity HBCUs MATTER! @attorneycrump • Exactly. The misconception that affirmative action meant unqualified people have been admitted into college solely because of their race was never true and is quite frankly an ignorant interpretation. Thank you @joyannreid for setting the record straight and sharing your truth! #andthisiswhyweshouldgotohbcus #hbcusmatter #blackexcellence ♬ original sound - African Heritage City The USA wasn't started to be a place of fairness or equality or any similar positives and it can't change to be those.
Black people have wasted a lot of time trying to make the USA what it will never be
-
phantom lady 1944 - portrait of ella raines - photography alamy
Column: How profit-driven turmoil at Turner Classic Movies placed a vast cultural heritage at risk
Michael Hiltzik
June 29, 2023
It wasn't that long ago that the cause of film preservation and film history seemed to be on a roll. Multiple cable channels such as American Movie Classics, Bravo and Encore were devoted to classic films from the 1930s through the 1980s. When streaming supplanted scheduled cable programming, FilmStruck offered viewers a huge library of classics from the libraries of Warner Bros. and other studios.
Through it all Turner Classic Movies, or TCM, was the much-admired king. The channel was founded in 1994 by entrepreneur Ted Turner to show the library of MGM classic films he had acquired. It evolved to not only screen classic films but also curate its offerings, providing historical commentaries and interviews presented by knowledgeable hosts.
All those other services have either disappeared or been repurposed away from classic films. Until a couple of weeks ago, TCM appeared to be one of the sole survivors in the classic movie landscape.
Bruce Goldstein, Film Forum
But on June 20, David Zaslav, chief executive of TCM's new owner, Warner Bros. Discovery, swung the ax. Layoffs wiped out the network's entire top management, including some figures who had been its leaders for decades. TCM was placed under the supervision of an executive whose other responsibilities included the Adult Swim channel and Cartoon Network.
The sense of dismay and betrayal that swept across Hollywood was almost indescribable. Film stars and character actors known to millions of fans took to social media to condemn the move. Film directors Steven Spielberg, Paul Thomas Anderson and Martin Scorsese reached out to Zaslav to urge him to back off, advice he seems to have taken, partially.
The turmoil at TCM points to more than a single company's effort to squeeze as much profit as possible from a single asset. It reflects the impulse by the corporate stewards of America's immense film history to view that culture strictly in commercial terms.
"Whether Mr. Zaslav planned to or not, he has inherited an American cultural treasure that he is responsible for safeguarding," film historian Alan K. Rode, a director of the Film Noir Foundation, told me. "But he's also trying to run a business that's over $40 billion in debt. I don't know how you square that circle."
This is not a new conundrum. Almost all artifacts of film history are squirreled away in studios' vaults, where they've been subject to the vicissitudes of corporate accounting and the ebb and flow of mergers and acquisitions.
Occasionally, when they're encouraged by cultural fashions or the appearance of new technologies, the studios have burrowed into their film libraries to assess their marketability and try to untangle ownership rights.
Some 700 historic Paramount Studios productions, for example, are assumed to be nestled in the vaults of Universal Pictures, which inherited Paramount’s 1930s and 1940s film archive from its forebear MCA, which acquired the collection in 1958. (Universal was later absorbed by NBC and is now a division of the entertainment conglomerate Comcast.)
The studios don't repurpose their libraries wholesale. Converting old films to digital formats to be screened online or on cable, or shown in theaters equipped with digital projectors, is an expensive and complicated process. Only films thought to have commercial potential get the favored treatment. Most of the others remain largely inaccessible to the public.
Warner Bros., now absorbed into Warner Bros. Discovery, was long considered the best steward of its cultural hoard. Its Warner Archives division was the industry gold standard in the care and marketing of the past. Under division head George Feltenstein, now the Warner library historian, Warner put thousands of titles, including TV series, on sale as made-to-order DVDs and established a subscription video streaming service that has since been incorporated into the company's Max streaming service.
Choosing which films to market as DVDs or Blu-ray discs was sometimes an easy call, sometimes a challenge, Feltenstein told me in 2015. “There always will be a place on the retail shelf for ‘Casablanca,’ ‘King Kong’ or ‘Citizen Kane,’” he said. But others required finer judgments or innovative marketing. Warner Bros. still offers DVDs and Blu-rays from its classic and contemporary libraries for sale.
Classic-film cable and streaming services have tended to have short half-lives. Consider the fate of FilmStruck, which launched as the subscription-based streaming arm of Turner Classic Movies in November 2016 with an inventory of 500 films, including 200 from the classic movie library of the Criterion Collection. FilmStruck quickly became what Esquire termed "the new go-to movie destination for serious movie buffs."
Two years later, FilmStruck was dead, slain by Warner Bros.' new owner, AT&T, which couldn't wait for the service to grow beyond its base of 100,000 subscribers and reach profitability. For AT&T, as I wrote then, "mass subscribership and profits are the ballgame," patience be damned.
Other networks that had been founded to cultivate an audience of film fans suffered a similar fate. American Movie Classics was founded in 1984 as a premium cable channel to air classic films uncut and commercial-free. It even sponsored an annual film festival to raise money for film preservation. In 2002 it was rebranded as AMC and refocused on prestige TV. AMC produced "Breaking Bad" and "Mad Men," among other series — good TV, certainly, but not classic films.
AMC's sister channel, Bravo, was launched in 1980 to present classic foreign and independent films. After NBC bought it in 2002, it was turned into a showcase for reality series.
Yet audience interest in classic movies and film history continued to grow. "Ten years ago, I felt that we were in kind of a golden age of appreciation of film classics and appreciation, and TCM was a huge part of that," says Bruce Goldstein, the founding repertory artistic director of Film Forum, a New York repertory house. "Now it seems to be falling apart."
TCM and the Criterion Channel remain the go-to streaming destinations for classics. Netflix, am*zon Prime and other networks have minimal classic libraries and no learned curation.
On the surface, there is no great mystery about why Warner Bros. Discovery and Zaslav might want to draw in their financial horns a bit. The company is laboring under a crippling debt load of more than $49 billion, most of it resulting from the 2022 merger that brought together the cable programming company Discovery and the WarnerMedia division of AT&T, itself the product of AT&T's 2016 takeover of Time Warner.
Given the combined companies' loss of $7.4 billion on revenue of $33.8 billion last year, plainly something had to give. The question being asked by cultural historians, cinephiles and plain ordinary film fans is why TCM had to be part of the bloodletting. It was reportedly profitable, if not hugely so, but by any measure not a significant factor on the merged company's profit-and-loss landscape.
That low profile in corporate terms could be TCM's salvation. As my colleague Stephen Battaglio reported, an outcry in the film industry, including by Spielberg, Anderson and Scorsese, has prompted Zaslav to reassess the bludgeoning he visited upon TCM.
The network's longtime programming chief, Charles Tabesh, who had been fired, will stay on, TCM says. Spielberg, Anderson and Scorsese will have a voice on TCM's curation and scheduling. TCM's classic film festival, held annually in Hollywood, will continue. In a move aimed at quelling outrage in the industry, the network will report directly to Warner Bros. Pictures Group co-heads Michael De Luca and Pamela Abdy.
Those developments generated an optimistic joint statement from Spielberg, Anderson and Scorsese: “We have already begun working on ideas with Mike and Pam, both true film enthusiasts who share a passion and reverence for classic cinema that is the hallmark of the TCM community," the directors said.
It's impossible to overstate the reverence that film historians and preservationists, and fans, have felt for TCM.
"They are the keepers of the flame," says Foster Hirsch, a professor of film at Brooklyn College and member of the Film Noir Foundation board. "They're an enormous resource for scholars and writers and fans of all ages. To start tampering with the brand or to view it in terms of marketing and data exclusively is horrifying. It's an assault on our common culture."
Among TCM's virtues is its eclectic approach. "They didn't show only well-known masterpieces," Hirsch says. "They showed obscure films, some which aren't good, they showed films for almost all tastes, different genres. From an artistic or historical point of view it isn't broken. There was no reason to 'fix' it."
The network has also been an almost unique portal introducing new generations to film culture. "It's been an essential part of people's film education, especially people of my generation," says Jon Dieringer, 37, founder of Screen Slate, a film culture website. "I grew up watching Turner Classic Movies."
Yet how assiduously Warner Bros. Discovery will follow through on its stated commitment to TCM's mission remains open to question, as does whether the network can retain its stature in the cinephile community. The confidence that the network's fans had in its staff and hosts and their ability to provide a curated approach to film history has been deeply shaken.
Many in the film community are hoping that TCM may have suffered nothing more serious than a near-death experience. Whether that's so won't be known for some time. Everyone will be watching, but experience suggests that when public companies pledge to treat the cultural assets under their control as more than generators of cash and profits, it's wise to expect the worst.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/column-profit-driven-turmoil-turner-120049275.html
Too many classic films remain buried in studios’ vaults
BY MICHAEL HILTZIKBUSINESS COLUMNIST
OCT. 23, 2015 5:48 PM PT
Will McKinley, a New York film writer, is dying to get his hands on a copy of “Alias Nick Beal,” a 1949 film noir starring Ray Milland as a satanic gangster. For classic film blogger Nora Fiore, the Grail might be “The Wild Party” (1929), the first talkie to star 1920’s “It” girl Clara Bow, directed by the pioneering female director Dorothy Arzner. Film critic Leonard Maltin says he’d like to score a viewing of “Hotel Haywire,” a 1937 screwball comedy written by the great comic director Preston Sturges.
Produced by Paramount Studios, these are all among 700 titles assumed to be nestled in the vaults of Universal Pictures, which inherited Paramount’s 1930s and 1940s film archive from its forebear MCA, which acquired the collection in 1958. They’re frustratingly near at hand but out of reach of film fans and cinephiles.
Like most of the other major studios, Universal is grappling with the challenging economics of making more of this hoard accessible to the public on DVD, video on demand or streaming video. Studios have come to realize that there’s not only marketable value in the films, but publicity value in performing as responsible stewards of cultural assets.
I would have to break the law to see that film.
— Cinephile Nora Fiore, of a 1932 classic locked in a studio vault
No studio recognizes these values better than Warner Bros., whose Warner Archives division is the industry gold standard in the care and marketing of the past. The studio sells some 2,300 titles, including TV series, as made-to-order DVDs and offers its own archival video streaming service for a subscription fee of up to $9.99 a month.
The manufacturing-on-demand service, launched in March 2009 with 150 titles, has proved “far more successful than we even dreamed,” says George Feltenstein, a veteran home video executive who heads the division. “I thought that all the studios would follow in our footsteps, but nobody has been as comprehensive as we’ve been.”
Other major studios have dipped their toes into this market, if gingerly. Paramount last year stocked a free YouTube channel with 91 of its own titles, mostly post-1949. This month 20th Century Fox announced that as part of its 100th anniversary this year, it would release 100 remastered classic films, including silents, to buy or rent for high-definition streaming — “enough to make any classic film fan weep with joy,” McKinley wrote on his blog. Sony last year introduced a free cable channel, get.tv, to screen films from its Columbia Pictures archive, though it’s only spottily available and often preempted by cable operators.
Universal offers some manufacture-on-demand titles via am*zon as its Universal Vault Series and announced in May that it would restore 15 of its silent films as part of its 2012 centennial celebration. Curiously, Universal, owned by the cable giant Comcast, is one of the only majors without a dedicated cable channel or Internet streaming service for its archive. Universal spokesperson Cindy Gardner maintains that the studio is working on ways to improve: “Stay tuned.”
Film buffs and historians have easier access to more classic films than ever before. But that only whets their appetite for important — but perhaps forgotten — films.
The 1932 Paramount World War I drama “Broken Lullaby,” Fiore says, might provoke a reexamination of the career of its director, the master of graceful comedy Ernst Lubitsch. But a version that crept onto YouTube a few years ago was taken down at the insistence of Universal. “I would have to break the law to see that film,” laments Fiore, who blogs on classic films in the guise of the Nitrate Diva.
“The studios seem to be sitting on a lot of films, but they’re limited by budget and by their projected return on investment,” says Alan Rode, a director of the Film Noir Foundation. “But it’s not like you open a valve and films come gushing out. If they can’t realize a profit on it, they’re not going to do it.”
Adding to the challenge is that some of the major studios have become subsidiaries of large corporations, and not consistently huge profit centers. For example, Paramount last year contributed about 26% of the $13.8 billion in revenue of its parent, Viacom, but its $205 million in operating profit paled next to the $2.4 billion net income recorded by the whole corporation.
Converting a film title for digital release can be costly, especially under the watchful eye of cinephiles who demand high quality. Some black-and-white titles can be digitized for $40,000 or less, says Jan-Christopher Horak, director of the UCLA Film & Television Archive — with 350,000 titles, the second-largest in the U.S. after only the Library of Congress.
But the price rises exponentially for color, especially for important restoration. UCLA spent about three years and $1.5 million in donated funds on its heroic restoration and digital transfer of the Technicolor classic “The Red Shoes,” a 1948 backstage ballet drama revered for its beauty.
That means that when deciding which titles to prepare for digital release, archive managers must walk a tightrope between serving their audience and protecting the bottom line. Some classics are easy calls. “There always will be a place on the retail shelf for ‘Casablanca,’ ‘King Kong’ or ‘Citizen Kane,’” says Warner’s Feltenstein. But finer judgments are required for what Feltenstein calls “the deeper part of the library.”
“My job is to monetize that content, make it available to the largest number of people possible and do so profitably,” Feltenstein told me. To gauge demand, Feltenstein’s staff keeps lines open with film enthusiasts and historians via Facebook, Twitter, a free weekly podcast and other outreach. “They literally ask us, ‘What do you want to see?’” Fiore says.
That gives them a window into values that others might miss. Take B-movie westerns made in the 1940s and 1950s that landed in the Warners vault. To Allied Artists and Lorimar, their producers, “these films were worthless and they said it’s OK to let them rot,” Feltenstein says. Instead, Warner Archives packaged them into DVD collections, “and they’ve all been nicely profitable.”
Feltenstein says Warners is releasing 30 more titles to its manufacturing-on-demand library every month. “It’s growing precipitously and there’s no end in sight.” Universal’s Gardner says there’s “real momentum” at her studio behind “making our titles more available than ever before.”
But there’s always more beckoning over the horizon. “The good news is that every studio is actively engaged in taking care of its library,” Maltin says. “That’s a big improvement over 20 or 25 years ago. But access is the final frontier.”
[UPDATE: Nell Minow, whose excellent blog on film can be found at Movie Mom and who is a fan of “Alias Nick Beal,” reports that the title character, played by Ray Milland, is more than merely a “satanic gangster” as we describe him above--he’s Satan.]
Michael Hiltzik’s column appears every Sunday. His new book is “Big Science: Ernest Lawrence and the Invention That Launched the Military-Industrial Complex.” Read his blog every day at latimes.com/business/hiltzik, reach him at mhiltzik@latimes.com, check out facebook.com/hiltzik and follow @hiltzikm on Twitter.
https://www.latimes.com/business/hiltzik/la-fi-hiltzik-20151025-column.html
-
My final preaching on black leadership in the usa in AALBC hopefully
MY THOUGHTS
I said all this before in this very forum but I am too lazy to find and cite myself. so i apologize for preaching
QuoteWho are the Leaders of the Black Community?
The Black community has a global existence which is intramultiracial, various regional existences<caribbean/south asia/africa/> each intramultiracial, an existence under each flag<usa/cuba/brazil/ghana/germany/pakistan/phillipines/australia> most intramultiracial.
This is the same for all phenotypical races.
Under the USA, the black community is highly intramultiracial: DOS/Jamaican/haitian/colombian/brazilian/nigerian/ghanaian/south african/indian/phillipino/ plus many more. And many of said groups are intramultiracial.
So, the question who are the leaders of the black community requires specification cause the black community is different based on the geographic scope you are approaching it with.
To be blunt, what the black community in nigeria need is not the same as in jamaica or the same as in phillipines.
So my answer is specific to the black community in the usa. I repeat , the following is specific to the black community in the usa.
Now to answer, the black community in the usa doesn't have a leader as a group or individual. But, in defense , this is all communities in the usa. The USA multiracial quality is so high no group or community has a leader, as every community or group in the usa has within it tribes or factions that just can't work together based on what they truly want. Ala even the white community in the usa is fractured. The reality is some whites want a return to a form of white power in the usa as well as a different posture of the usa in international affairs that other whites for various reasons don't want and no middle ground exist. It is that simple.
The same to the black community in the usa, which has historically always been multivided in unbridgeable chasms, always, from the very start of the usa. The only problem is black people who knew this didn't teach this to black children, they lied about the nature of the black community in the usa for their own agenda. Thinking foolishly that over time the truth can be undone. The truth always wins in the end.
QuoteOver the years there have been many conversations on this forum about how Black people should pool our resources, support our businesses, and control our destiny.
At this point in time I will merely restate what I said in this forum, apologize for not citing myself.
Black people in the usa need to focus on their tribes in the village and get said tribes to be efficient in that way. As I always say to Black elephants <republicans> or Black militants or Black donkeys<democrats> or Black socialists or Black garveyites or Rastafarians or Black baptists or Black catholics or others <I know nearly every black tribe being in nyc> They talk so much about what other black people need to do but never seem to be able to do something within their own tribe.
For example, the Black Elephants go on and on about financial responsibility and yet I can't recall the black elephants showing the rest of the black community their great acumen for financial responsibility to help the black community in the usa. Another example, Black Donkeys go on and on about voting but and yet I can't recall the black elephants showing the rest of the black community how effective voting will be to help black community in the usa.
Black people in various tribes in the village in the usa love complaining about what the whole community isn't doing while their tribe is doing nothing. Wealthy black entertainers couldn't even unite and make it where BET/Motown/Philadelphia international are black owned global media brands.
QuoteIn the past, civil right organizations lead the charge in organizing successful boycotts and getting important legislation passed. Today these organizations are a shell of what they once were -- toothless.
Well, the NAACP was white jew financed and served its purpose. And black financiers pre civil rights act had many of their financial revenue streams destroyed by the inevitable result of the civil rights act. Absent money, most organizations are like the people above complaining about what the community isn't doing while they do nothing.
QuoteSocial media is seen by many as the modern way to mobilize Black people. I've always lamented the fact that we hitch our wagons to platforms we do not own or control and claim it as a tool to support Black people. This was always a flawed strategy. "Black Twitter" was a recent example of this. I'd go farther and say that the entire social media universe not only does not serve Black people; it is harmful to us.
do most in the black community want potent <note I didn't say positivit> effective leadership ? yes. Do most individuals in the black community think they are that leader ? no. in absence of potent effective leadership are people in the black community making false leaders? yes.
But all communities go through this. Now their is a historical issue here.
Many black leaders in the past, ala Frederick Douglass, embraced the idea of hyper individualism. Individualism in its most intense form, is against communal growth. The idea is the individual do for self, regardless of community. why blakc leaders in the past support this? Individualism is the answer to getting a multiracial populace to operate absent biases. Race will never leave humanity , calling yourself a name is a racial act, but bias is when people favor based on race. Individualism lessens biases ability to bind groups by the focus on the individual.
To that end the black community through guidance of some black leaders side the external white manipulation have embraced the individualism.
QuoteIn the past, any organization that has shown a sign effectively mobilizing Black people from the Universal Negro Improvement Association to The Black Panther Party even the Nation of Islam, was actively undermined by our government.
Yes, any organization that functionally demanded some level of black segregation was an enemy to not only the federal government , who started the Federal Bureau of Investigation for the original KKK who had plans on making a shadow government in the usa,but organizations like the naacp financed by white jews.
QuoteObviously, our current lack of organization is not only a consequence of direct attacks against our organizations, but several hundreds of years of violent and legalized oppression.
and our own manipulations to ourselves.
QuoteToday are we completely rudderless as a people? Who, or what organization, could initiate a Montogomery Bus Boycott today? Are we so happy today that a boycott is completely unnecessary? Which organization could do what the NAACP Legal Defense Fund did to win Brown v. Board of Education, or are we happy that "race" can no longer be used to help reverse hundreds of years of being prevented from learning to read, while benefits to white people like legacy admissions continue?
Yes, in modernity, black leaders to the community in the usa, are absent. But, a why exists. It isn't unimportant how intramultiracial the black community is. Yes, all humans are humans. Yes, all black people are black people but people or humans all too often do want different things in the subtlely. The Sons of Odin want jobs and wealth but they wouldn't mind depriving blacks. Do Black Christians really want to embrace the black lgbtq+ community? I say no.
Most Black people are not happy in the usa, but most black people have accepted the individual mantra, that black leaders often utter. Black people talk community, but most of us don't feel community, most from each of us feel one against the world. Again, Community has to be exhibited, not just talked about.
In the usa, The leaders of the black community today or a tomorrow have to lead effectively, but have to be able to give a hand to the doubtful blacks who are convinced correctly that black leaders don't uplift but merely tell other blacks to lift themselves. Black people have seen way too many black leaders help themselves and tell other blacks to lift themselves up by bootstraps to be convinced even with one great showing that a leader is actually trying to help left their bootstrapless selves up.
-

1)what has to improve in how individualism works in said community?
In my mind one point. The one thing I hear no one say... Own up to it. It may sound silly but one of the biggest problems in the usa is people don't own up to their own culture that their actions display.Black folk like me will always despise the KKK But, the KKK are better than the majority of whites who clearly dislike black people as negatively as the KKK but are too proud to admit it. If you are about you, just say it. No shame in saying, I am looking out for me while all you do is look out for you. But the black community or the larger human populace in the usa suffers from an inability to admit in public what their actions show. The faux communal discourse form hyper individuals to me is the problem. I don't have a problem with anyone , and that starts with black people, being about themselves. I follow my own path. I like being communal. but I also profess my position publicly. I am not ashamed to say I like living around black folks and prefer living around black folks, and I don't care for living aside non blacks <as I define blacks side non blacks>. But too many individualists are not ashamed to act for only self but are ashamed to advertise it. That will be a nice change.
2)What inevitable weaknesses come from such a system that need to be expected or embraced as truth?
a dysfunction of the way... all ways have dysfunction. Communalism's great problem is it doesn't allow for individual growth at the same rate or width or uniqueness as individualism. But, Individualism's problem is it doesn't allow for collective action or interaction at the same rate width or flexibility as communalism.
-
-
Illustration by Sam Whitney/The New York Times
Pedro Pascal and Jenna Ortega Shouldn’t Be Exceptions in Hollywood
July 23, 2023
By Arlene Dávila
Ms. Dávila is the founding director of the Latinx Project at New York University.
Corporate America’s treatment of Latinx people as a homogeneous monolithic group, instead of the diverse demographic it is, has for decades perpetuated stereotypes of Latino authenticity. These stereotypes have disproportionately depicted Latinos on TV and in movies as Spanish speakers that hailed from Latin America and shared a particular Latin “look.”
In Hollywood, this narrative has reinforced the notion that we are a niche market that is separate from the mainstream, which could be served through the importation of programming that is cheaper to produce in Latin America over programming that is produced in the United States.
That’s why it was exciting to see Jenna Ortega and Pedro Pascal make Emmy history this month. For the first time two Latino actors were nominated in the lead acting category in the same year, for the hit shows “Wednesday” and “The Last of Us.”
Though Latinx people make up 19 percent of the U.S. population, they account for less than 5 percent of actors cast in speaking roles in the nation’s top-grossing films. Additionally, representation in the media industry as a whole stands at a mere 12 percent, with the majority of positions being service oriented, like cleaning services and security. These numbers have remained stagnant for decades, which is outrageous when you consider that they make up nearly half the population of Los Angeles County.
Why has the media industry been so unwilling to acknowledge and address this growing demographic of potential viewers and consumers?
Latinx creatives have told me that many executives in Hollywood don’t understand why they are outraged by how few Latinx people appear in films and television shows. After all, there is already a variety of streaming offerings from Latin America and Spain. But there is a profound difference between these markets.
We wouldn’t mistake the experience of Indigenous Mexicans living in Mexico for the experience of a fifth-generation Chicana. This is why many in the industry are identifying as Latinx — a term that signals gender inclusivity and recognition of our racial and ethnic diversity — to call attention to a pattern of exclusion of Latinx writers and creators that are representing the U.S. experience.
The globalization of Spanish language media has only widened the existing gaps between the robust development of movies and shows produced in Latin America and the limited opportunities for Latinx writers, directors and showrunners in the United States. In recent decades, Latin American media companies have benefited from investments from American streaming conglomerates like Netflix, the lower costs of producing and importing programming in Latin America and investments by governments in the region that support their film industries.
While streaming platforms offer a wealth of series and films from Spain and Latin America, there is a lack of representation of stories written by Latinx people that reflect their experiences. While actors and writers from Latin America have had the opportunity to expand their résumés with credits from global serials produced by platforms like Netflix, am*zon and Max, Latinx actors and audiences have fewer roles to choose from. The leads cast in series like “Wednesday” and the “Last of Us” are rare exceptions.
Research shows that in the United States, Latinx actors are often cast in the roles of lower-class characters, criminals or immigrants. The gap is wider still for Afro-Latinos. In shows produced in Latin America, the majority of actors cast as leads and heroines are blond and white, while darker-skinned actors are often relegated to secondary roles, housekeepers or criminals, if they are represented at all. Additionally, Latinx writers face extra barriers when entering a shrinking industry, as highlighted by the writers’ strike.
The few productions that have been written or created by Latinx people and have represented our communities in real and personal ways have been canceled after a few seasons. When shows like “Gentefied,” “Vida” and the “Gordita Chronicles” were shut down despite positive reviews, writers and fans alike were left wondering why. In the age of streaming, algorithm-driven decisions make it difficult to determine what counts as success with transparency, especially when algorithms are biased against new content.
Latinx audiences remain avid consumers of films, TV and other media, even if they don’t see themselves reflected. Some may question why media conglomerates should change and invest in original content and programming or cast Latinx actors and writers when the cheaper importation-based model is so profitable and seemingly successful. Yet they should evolve because those formulas have historically left Latinx audiences mostly untapped. There are generations of talented scriptwriters, producers and filmmakers who have been underutilized and countless rich stories and ideas that have yet to be told. Film and TV that represent the experience of Latinx communities in the United States enrich the media ecosystem by offering a more accurate representation of American demographics.
Additionally, we must address the negative impacts of the media’s import-heavy formula for Latinx audiences, which limits opportunities and perpetuates the perception of Latinx people as foreigners rather than fellow Americans deserving equal visibility on television and movie screens.
It’s worth noting that Latinx people are not the only group excluded by the globalization of streaming. That Ms. Ortega and Mr. Pascal received recognition raises the question of whether we have reached a crucial turning point. It’s worth considering how we can leverage the current SAG-AFTRA and W.G.A. strikes to also address issues of representation and investment in productions that will provide working opportunities for Latinx actors, writers and showrunners alongside matters of pay equity for media workers.
Finally, it is time to consider the global appeal of entertainment featuring Latinx actors. I want to see more roles for actors like Ariana DeBose, the first Afro-Latina to win an Oscar, for a supporting role in “West Side Story,” and productions by filmmakers and MacArthur “genius grant” awardees Alex Rivera and Cristina Ibarra, among many other outstanding Latinx creatives.
I often wonder what it would look like if Hollywood dared to recognize that Latinx talent is not an exception.
Arlene Dávila, the founding director of the Latinx Project at New York University, is the author of “Latinx Art: Artists, Markets and Politics.”
URL
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/23/opinion/latinos-hollywood-representation.html

The recently released Barbie movie has provided an opportunity for a bipartisan coalition of commentators and elected officials to see value in its dissection.Credit...Kenny Holston/The New York Times, Gonzalo Fuentes/Reuters, Jim Wilson/The New York Times, Alex Brandon/Associated Press, Warner Bros. Pictures via Associated Press
‘Barbie’ Movie Gives Left and Right Another Battlefront, in Pink
Political figures of all types grabbed for the legs of a doll-turned-movie-turned-cultural moment, with predictable results.
By Matt Flegenheimer and Marc Tracy
Last week, Representative Matt Gaetz and his wife, Ginger, arrived at a Washington reception for “Barbie” in matching pink, grinning in photos along the “pink carpet,” mingling among guests sipping pink cocktails, admiring a life-size pink toy box.
They left with political ammunition.
“The Barbie I grew up with was a representation of limitless possibilities, embracing diverse careers and feminine empowerment,” Mrs. Gaetz wrote on Twitter. “The 2023 Barbie movie, unfortunately, neglects to address any notion of faith or family, and tries to normalize the idea that men and women can’t collaborate positively (yuck).”
When another account scolded Mr. Gaetz, the hard-right and perpetually stunt-seeking Florida congressman, for attending the event at all — citing the casting of a trans actor as a doctor Barbie — Mr. Gaetz replied with a culture-warring double feature.
“If you let the trans stop you from seeing Margo Robbie,” he said, leaving the “T” off the first name of the film’s star, “the terrorists win.”
The non-terroristic winners were many after the film’s estimated $155 million debut: Ms. Robbie and Greta Gerwig, the film’s director, finding an eager audience for their pink-hued feminist opus; the Warner Bros. marketing team, whose ubiquitous campaigns plainly paid off; the film industry itself, riding “Barbie” and “Oppenheimer” to its most culturally dominant weekend in years.
But few outcomes were as nominally inexplicable (and probably inevitable) as the film’s instant utility to political actors and opportunists of all kinds. For a modern take on what was long a politically fraught emblem of toxic body image and reductive social norms, no choice was too small, no turn too ideology-affirming or apparently nefarious, for a bipartisan coalition of commentators and elected officials to see value in its dissection.
“I have, like, pages and pages of notes,” Ben Shapiro, the popular conservative commentator, said in a lengthy video review, which began with him setting a doll aflame and did not grow more charitable. (He said his producers “dragged” him to the theater.)
“I took a tequila shot every time Barbie said patriarchy … only just woke up,” wrote Elon Musk. (Mr. Shapiro, diligently but less colorfully, said he had counted the word “more than 10 times.”)
“Here are 4 ways Barbie embraces California values,” the office of Gavin Newsom, the state’s Democratic governor, wrote in a thread hailing Barbie as a champion of climate activism, “hitting the roads in her electric vehicle,” and of destigmatizing mental health care.
If there was a time in the culture when a giant summer film event was something of an American unifier — a moment to share over-buttered popcorn through big-budget shoot-’em-ups and sagas of insatiable sharks — that time is not 2023.
And, as ever, the political class’s performative investment in “Barbie” — the outrage and the embrace — can seem mostly like a winking bit.
What to make of Gov. Gretchen Whitmer, Democrat of Michigan, posting a Barbie meant to resemble herself beside the Instagram caption, “Come on Barbie, let’s go govern”?
What does it mean, exactly, when Senator Raphael Warnock, Democrat of Georgia, says of himself, “This Ken is pushing to end maternal mortality”?
Certainly, Senator Ted Cruz, Republican of Texas, has summoned practiced gravity in accusing “Barbie” of working to appease the Chinese. (Some Republicans have fixated on a scene that features a crudely drawn map that supposedly depicts the so-called nine-dash line, which indicates Chinese ownership of oceanic territory that is disputed under international law. Vietnam has banned showings of the movie in the country over that image.)
“Obviously, the little girls that are going to see Barbie, none of them are going to have any idea what those dashes mean,” Mr. Cruz told Fox News. “This is really designed for the eyes of the Chinese censors, and they’re trying to kiss up to the Chinese Communist Party because they want to make money selling the movie.”
The response on the right is not a one-off. For a generation of conservative personalities, weaned on Andrew Breitbart’s much-cited observation that “politics is downstream of culture,” Hollywood and other ostensibly liberal bastions are to be confronted head-on, lest their leanings ensnare young voters without a fight.
Recent years have provided ample evidence, some on the right say, for a “go woke, go broke” view that progressivism is bad business. Last year’s apolitically patriotic “Top Gun: Maverick” was a smashing success, as was this year’s kid-friendly “The Super Mario Bros. Movie.” By contrast, critics on the right contended that Disney’s remake of “The Little Mermaid,” with its title character portrayed by the Black actress Halle Bailey, failed to match its producers’ hopes. (Of course, there is no way to trace exactly what determines any movie’s success or failure, and many observers adhere to the screenwriter William Goldman’s axiom: “Nobody knows anything.”)
“Barbie” cannot be said to have gone broke. But its purported politics, conservatives have argued, did damage it by making it less entertaining — “a lecture,” in the words of The Federalist’s Rich Cromwell, “that self-identifies as a movie.”
Kyle Smith, a reviewer at The Wall Street Journal, complained that the film “contains more swipes at ‘the patriarchy’ than a year’s worth of Ms. magazine.”
The film seems at times (gentle spoiler alert) to be engaging with “the patriarchy” ironically, infusing it with knowing Southern California vapidity, décor that seems inspired by hair metal and a heavy emphasis on weight lifting and “brewskis.”
When it comes time (less gentle spoiler alert) to reclaim Barbie Land, the Barbies distract the Kens by indulging their tendency for exaggerated gestures of malehood like playing acoustic guitar and insisting on showing a date “The Godfather” while talking over it.
Mr. Shapiro has sounded unconvinced that the movie is broadly in on its own jokes.
“The actual argument the movie is making is that if women enjoy men, it’s because they have been brainwashed by the patriarchy,” he said in his review.
He called the film, with a straight face, two hours he will rue wasting as he sits on his deathbed.
“The things I do,” he said, “for my audience.”
Anjali Huynh contributed reporting.
Matt Flegenheimer is a reporter covering national politics. He started at The Times in 2011 on the Metro desk covering transit, City Hall and campaigns. More about Matt Flegenheimer
Marc Tracy is a reporter on the Culture desk. More about Marc Tracy
ARTICLE URL
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/24/us/politics/barbie-movie-newsom-gaetz.html